Page 106 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 106
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
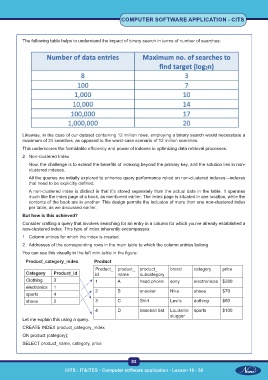
The following table helps to understand the impact of binary search in terms of number of searches:
Likewise, in the case of our dataset containing 12 million rows, employing a binary search would necessitate a
maximum of 24 searches, as opposed to the worst-case scenario of 12 million searches.
This underscores the formidable efficiency and power of indexes in optimizing data retrieval processes.
2 Non-clustered Index
Now, the challenge is to extend the benefits of indexing beyond the primary key, and the solution lies in non-
clustered indexes.
All the queries we initially explored to enhance query performance relied on non-clustered indexes—indexes
that need to be explicitly defined.
A non-clustered index is distinct in that it’s stored separately from the actual data in the table. It operates
much like the index page of a book, as mentioned earlier. The index page is situated in one location, while the
contents of the book are in another. This design permits the inclusion of more than one non-clustered index
per table, as we discussed earlier.
But how is this achieved?
Consider crafting a query that involves searching for an entry in a column for which you’ve already established a
non-clustered index. This type of index inherently encompasses:
1 Column entries for which the index is created.
2 Addresses of the corresponding rows in the main table to which the column entries belong.
You can see this visually in the left mini-table in the figure:
Product_category_index Product
Product_ product_ product_ brand category price
Category Product_id id name subcategory
Clothing 3 1 A head phone sony electronices $280
electronics 1
sports 4 2 B sneaker Nike shoes $70
shoes 2 3 C Shirt Levi’s dothing $50
4 D baseball bat Louisville sports $100
slugger
Let me explain this using a query.
CREATE INDEX product_category_index
ON product (category);
SELECT product_name, category, price
93
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer software application - Lesson 18 - 36