Page 90 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 90
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
CREATE INDEX idx_name_age
ON employees (last_name, age);
4 Monitor and Maintain Indexes
After adding indexes, it’s essential to monitor their performance over time. Regularly analyze query execution
plans to ensure that the indexes are being used as expected. Additionally, you may need to perform index
maintenance tasks like rebuilding or reorganizing indexes to optimize performance as data changes.
5 Consider Index Size
Keep in mind that indexes consume storage space. Too many indexes or indexing large columns can
significantly increase storage requirements. Balance the benefits of improved query performance against the
storage costs.
6 Drop or Modify Indexes
If you find that an index is not being used or is no longer necessary, you can drop it using the ‘DROP INDEX’
statement:
DROP INDEX index_name;
You can also modify existing indexes, such as adding or removing columns from composite indexes, depending
on your DBMS.
7 Test Query Performance
Before and after adding indexes, test the performance of your queries to ensure that they have indeed
improved. Profiling tools and query execution plans can help you evaluate the effectiveness of your indexing
strategy.
Concepts of Transactions
A transaction is a fundamental concept in DBMS that represents a unit of work involving one or more database
operations (e.g., INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT). Here are some key concepts associated with transactions:
Properties of Transaction (ACID Properties)
To carry out a transaction within a Database Management System (DBMS), it must exhibit a set of characteristics
commonly referred to as the ACID properties.
• A – Atomicity
• C – Consistency
• I – Isolation
• D – Durability
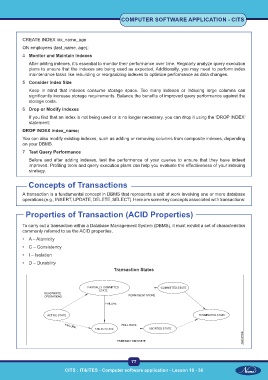
Transaction States
77
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer software application - Lesson 18 - 36