Page 198 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 198
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
60 Second 60 Second
Revolution
N
= 60/N Second/Revolution N Revolution
60
Second
Second
60
P = No. of poles; N Revolution
Revolution
N
N
A = No. of Parallel paths. N
60 60
N
In one revolution of the rotor each conductor 60
N
is cut by a flux of f P , 60 60 60
N N
60
Time for 1 revolution = Second
60
N
φP
Average emf induced per φPN N φP φPN
60 60 60 60
conductor /revolution = φP φPN N
N φP φPN
60 60
N 60 60
No.of conductors = Z φPN Z N φPN Z
60
a
No of parallel paths = a φPN Z 60 a
φPN
Z
60
Equation for induced emf = or E = φZN P
φZN
P
a
60 a R
60 a 60 a
φZN P
where a =P for lap and 2 for wave a60 φZN P
60 a
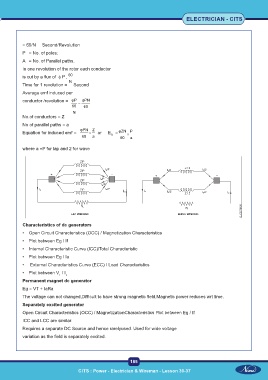
Characteristics of dc generators
• Open Circuit Characteristics (OCC) / Magnetization Characteristics
• Plot between Eg / If
• Internal Characteristic Curve (ICC)/Total Characteristic
• Plot between Eg / Ia
• External Characteristics Curve (ECC) / Load Characteristics
• Plot between V / I
T L
Permanent magnet dc generator
Eg = VT + IaRa
The voltage can not changed,Difficult to have strong magnetic field,Magnetic power reduces wrt time.
Separately excited generator
Open Circuit Characteristics (OCC) / MagnetizationCharacteristics Plot between Eg / If
ICC and LCC are similar.
Requires a separate DC Source and hence rarelyused. Used for wide voltage
variation as the field is separately excited.
185
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 30-37