Page 337 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 337
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Flasher
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• state the purpose of the flasher in the series lamp circuit.
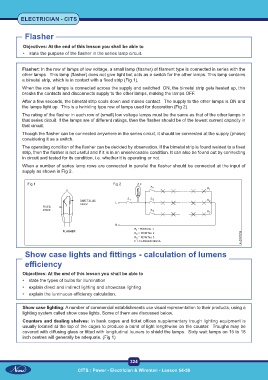
Flasher: In the row of lamps of low voltage, a small lamp (flasher) of filament type is connected in series with the
other lamps. This lamp (flasher) does not give light but acts as a switch for the other lamps. This lamp contains
a bimetal strip, which is in contact with a fixed strip (Fig 1).
When the row of lamps is connected across the supply and switched ON, the bimetal strip gets heated up, this
breaks the contacts and disconnects supply to the other lamps, making the lamps OFF.
After a few seconds, the bimetal strip cools down and makes contact. The supply to the other lamps is ON and
the lamps light up. This is a twinkling type row of lamps used for decoration (Fig 2).
The rating of the flasher in each row of (small) low voltage lamps must be the same as that of the other lamps in
that series circuit. If the lamps are of different ratings, then the flasher should be of the lowest current capacity in
that circuit.
Though the flasher can be connected anywhere in the series circuit, it should be connected at the supply (phase)
considering it as a switch.
The operating condition of the flasher can be decided by observation. If the bimetal strip is found welded to a fixed
strip, then the flasher is not useful and if it is in an unserviceable condition. It can also be found out by connecting
in circuit and tested for its condition, i.e. whether it is operating or not.
When a number of series lamp rows are connected in parallel the flasher should be connected at the input of
supply as shown in Fig 2.
Fig 1 Fig 2
Show case lights and fittings - calculation of lumens
efficiency
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• state the types of bulbs for illumination
• explain direct and indirect lighting and showcase lighting
• explain the luminuous efficiency calculation.
Show case lighting: A number of commercial establishments use visual representation to their products, using a
lighting system called show case lights. Some of them are discussed below.
Counters and dealing shelves: In bank cages and ticket offices supplementary trough lighting equipment is
usually located at the top of the cages to produce a band of light lengthwise on the counter. Troughs may be
covered with diffusing glass or fitted with longitudinal louvers to shield the lamps. Sixty watt lamps on 15 to 18
inch centres will generally be adequate. (Fig 1)
324
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 54-59