Page 63 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 63
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
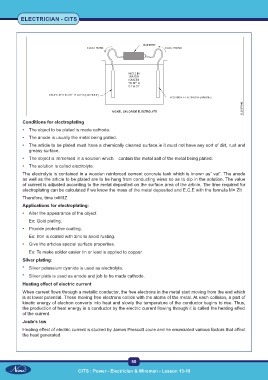
Conditions for electroplating
• The object to be plated is made cathode.
• The anode is usually the metal being plated.
• The article to be plated must have a chemically cleaned surface.ie it must not have any sort of dirt, rust and
greasy surface.
• The object is immersed in a solution which contain the metal salt of the metal being plated.
• The solution is called electrolyte.
The electrolyte is contained in a wooden reinforced cement concrete tank which is known as” vat”. The anode
as well as the article to be plated are to be hung from conducting wires so as to dip in the solution. The value
of current is adjusted according to the metal deposited on the surface area of the article. The time required for
electroplating can be calculated if we know the mass of the metal deposited and E.C.E with the formula M= ZIt
Therefore, time t=M/IZ
Applications for electroplating:
• Alter the appearance of the object
Ex: Gold plating.
• Provide protective coating.
Ex: Iron is coated with zinc to avoid rusting.
• Give the articles special surface properties.
Ex: To make solder easier tin or lead is applied to copper.
Silver plating:
* Silver potassium cyanide is used as electrolyte.
* Silver plate is used as anode and job to be made cathode.
Heating effect of electric current
When current flows through a metallic conductor, the free electrons in the metal start moving from the end which
is at lower potential. These moving free electrons collide with the atoms of the metal. At each collision, a part of
kinetic energy of electron converts into heat and slowly the temperature of the conductor begins to rise. Thus,
the production of heat energy in a conductor by the electric current flowing through it is called the heating effect
of the current.
Joule’s law
Heating effect of electric current is studied by James Prescott Joule and he enunciated various factors that affect
the heat generated
50
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 13-19