Page 77 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 77
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
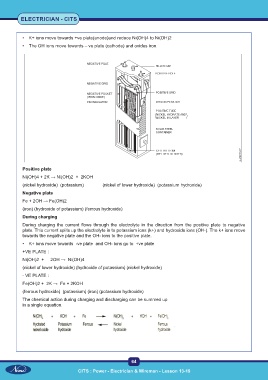
• K+ ions move towards +ve plate(anode)and reduce Ni(OH)4 to Ni(OH)2
• The OH ions move towards – ve plate (cathode) and oxides iron.
Positive plate
Ni(OH)4 + 2K → Ni(OH)2 + 2KOH
(nickel hydroxide) (potassium) (nickel of lower hydroxide) (potassium hydroxide)
Negative plate
Fe + 2OH → Fe(OH)2
(iron) (hydroxide of potassium) (ferrous hydroxide)
During charging
During charging the current flows through the electrolyte in the direction from the positive plate to negative
plate. This current splits up the electrolyte in to potassium ions (k+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The k+ ions move
towards the negative plate and the OH- ions to the positive plate.
• K+ ions move towards -ve plate and OH- ions go to +ve plate
+VE PLATE :
Ni(OH)2 + 2OH → Ni(OH)4
(nickel of lower hydroxide) (hydroxide of potassium) (nickel hydroxide)
- VE PLATE :
Fe(OH)2 + 2K → Fe + 2KOH
(ferrous hydroxide) (potassium) (iron) (potassium hydroxide)
The chemical action during charging and discharging can be summed up
in a single equation.
64
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 13-19