Page 84 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 84
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
The meter is having three colours red, yellow and green - red for fully discharged, yellow for half charge, green
for fully charged condition of the cell respectively.
The methods of charging the secondary cells are:
• constant current method
• constant potential method
• rectifier method.
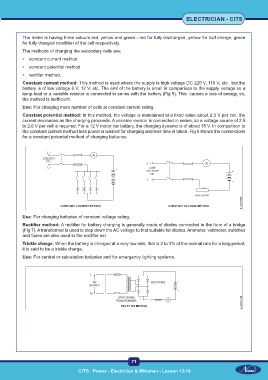
Constant current method: This method is used where the supply is high voltage DC 220 V, 110 V, etc. but the
battery is of low voltage 6 V, 12 V, etc. The emf of the battery is small in comparison to the supply voltage so a
lamp-load or a variable resistor is connected in series with the battery (Fig 5). This causes a loss of energy, so,
the method is inefficient.
Use: For charging more number of cells at constant current rating.
Constant potential method: In this method, the voltage is maintained at a fixed value about 2.3 V per cell; the
current decreases as the charging proceeds. A variable resistor is connected in series, so a voltage source of 2.5
to 2.6 V per cell is required. For a 12 V motor car battery, the charging dynamo is of about 15 V. In comparison to
the constant current method less power is wasted for charging and less time is taken. Fig 6 shows the connections
for a constant potential method of charging batteries.
Use: For charging batteries of constant voltage rating.
Rectifier method: A rectifier for battery charging is generally made of diodes connected in the form of a bridge
(Fig 7). A transformer is used to step down the AC voltage to that suitable for diodes. Ammeter, voltmeter, switches
and fuses are also used in the rectifier set.
Trickle charge: When the battery is charged at a very low rate, that is 2 to 3% of the normal rate for a long period,
it is said to be a trickle charge.
Use: For central or sub-station batteries and for emergency lighting systems.
71
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 13-19 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 13-19