Page 95 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 95
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
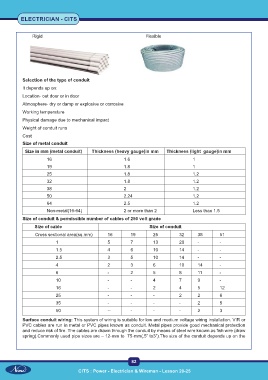
Rigid Flexible
Selection of the type of conduit
It depends up on:
Location- out door or in door
Atmosphere- dry or damp or explosive or corrosive
Working temperature
Physical damage due to mechanical impact
Weight of conduit runs
Cost
Size of metal conduit
Size in mm (metal conduit) Thickness (heavy gauge)in mm Thickness (light gauge)in mm
16 1.6 1
19 1.8 1
25 1.8 1.2
32 1.8 1.2
38 2 1.2
50 2.24 1.2
64 2.5 1.2
Non-metal(16-64) 2 or more than 2 Less than 1.5
Size of conduit & permissible number of cables of 250 volt grade
Size of cable Size of conduit
Cross sectional area(sq.mm) 16 19 25 32 38 51
1 5 7 13 20 - -
1.5 4 6 10 14 - -
2.5 3 5 10 14 - -
4 2 3 6 10 14 -
6 - 2 5 8 11 -
10 - - 4 7 9 -
16 - - 2 4 5 12
25 - - - 2 2 6
35 - - - - 2 5
50 -- - - - 2 3
Surface conduit wiring: This system of wiring is suitable for low and medium voltage wiring installation. VIR or
PVC cables are run in metal or PVC pipes known as conduit. Metal pipes provide good mechanical protection
and reduce risk of fire. The cables are drawn through the conduit by means of steel wire known as fish wire (draw
spring).Commonly used pipe sizes are – 12-mm to 75-mm(.5” to3”).The size of the conduit depends up on the
82
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 20-25