Page 248 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 248
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
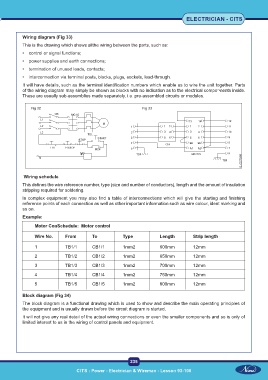
Wiring diagram (Fig 33)
This is the drawing which shows allthe wiring between the parts, such as:
• control or signal functions;
• power supplies and earth connections;
• termination of unused leads, contacts;
• interconnection via terminal posts, blocks, plugs, sockets, lead-through.
It will have details, such as the terminal identification numbers which enable us to wire the unit together. Parts
of the wiring diagram may simply be shown as blocks with no indication as to the electrical compo¬nents inside.
These are usually sub-assemblies made separately, i.e. pre-assembled circuits or modules.
Fig 32 Fig 33
Wiring schedule
This defines the wire reference number, type (size and number of conductors), length and the amount of insulation
stripping required for soldering.
In complex equipment you may also find a table of interconnections which will give the starting and finishing
reference points of each connection as well as other important information such as wire colour, ident marking and
so on.
Example:
Motor ConSchedule: Motor control
Wire No. From To Type Length Strip length
1 TB1/1 CB1/1 1mm2 600mm 12mm
2 TB1/2 CB1/2 1mm2 650mm 12mm
3 TB1/3 CB1/3 1mm2 700mm 12mm
4 TB1/4 CB1/4 1mm2 750mm 12mm
5 TB1/5 CB1/5 1mm2 800mm 12mm
Block diagram (Fig 34)
The block diagram is a functional drawing which is used to show and describe the main operating principles of
the equipment and is usually drawn before the circuit diagram is started.
It will not give any real detail of the actual wiring connections or even the smaller components and so is only of
limited interest to us in the wiring of control panels and equipment.
235
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 93-100