Page 259 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 259
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
3 Electric current
Electric Current The flow of (electricity) electrons in one direction along any path or around any circuit is called
electric current-Its symbol is / and its unit is ampere (A). The instrument by which the current is measured is called
an ampere meter which is always connected in series with the circuit-
4 Heating effect of electric current
Temperature and heat: In daily life, the terms heat and temperature are often used to mean the same thing. But
the terms are different in a technical sense. The difference between the two can, however, be easily clarified by
means of an example.
If 6 litres of water and 10 litres of water are heated separately on a hotplate for the same length of time, beginning
from the same initial temperature, then the same amount of energy has been supplied in each case. The end
temperature reached, however, will be different in the two cases. The smaller quantity of water will have a higher
end temperature, than the larger quantity of water.
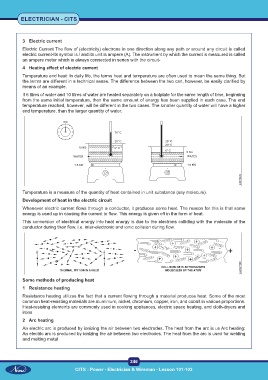
Temperature is a measure of the quantity of heat contained in unit substance (say molecule).
Development of heat in the electric circuit
Whenever electric current flows through a conductor, it produces some heat. The reason for this is that some
energy is used up in causing the current to flow. This energy is given off in the form of heat.
This conversion of electrical energy into heat energy is due to the electrons colliding with the molecule of the
conductor during their flow, i.e. inter-electronic and ionic collision during flow.
Some methods of producing heat
1 Resistance heating
Resistance heating utilizes the fact that a current flowing through a material produces heat. Some of the most
common heat-resisting materials are aluminium, nickel, chromium, copper, iron, and cobalt in various proportions.
Heat-resisting elements are commonly used in cooking appliances, electric space heating, and cloth-dryers and
irons
2 Arc heating
An electric arc is produced by ionizing the air between two electrodes. The heat from the arc is us Arc heating:
An electric arc is produced by ionizing the air between two electrodes. The heat from the arc is used for welding
and melting metal
246
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 101-103