Page 101 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 101
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
2 DC Chopper
DC chopper works on DC voltage. They work as a step up and step down transformers on DC voltage. They can
convert the steady constant DC voltage to a higher value or lower value based on their type.
DC choppers are more efficient, speed and optimized devices. These can be incorporated on electronic chips.
They provide smooth control over the DC voltage.
Different Types of Chopper Circuits:
The main element based on which choppers are categorized is the semiconductor used in the chopper circuit.
Based on the positioning of this semiconductor, choppers can be made to work in any of the four quadrant
conditions. Depending on the quadrant of operation choppers are categorized as Type A, B, C, D, and E
Type A chopper works in the first quadrant. In this chopper, the voltage and current both are positive and flows
in the same direction. Power from source to load and the average output voltage is less than input DC voltage.
Type B chopper works in the second quadrant. Here the load voltage is positive and current is negative. Power
flows from load to source. This chopper is also known as a step-up chopper.
Type C chopper is formed by parallel connection of Type A and Type B choppers.
Type D chopper is the two quadrant type B chopper and Type E chopper is the fourth gradient chopper.
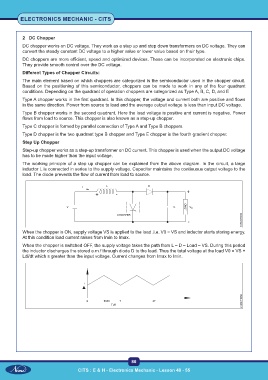
Step Up Chopper
Step-up chopper works as a step-up transformer on DC current. This chopper is used when the output DC voltage
has to be made higher than the input voltage.
The working principle of a step up chopper can be explained from the above diagram. In the circuit, a large
inductor L is connected in series to the supply voltage. Capacitor maintains the continuous output voltage to the
load. The diode prevents the flow of current from load to source.
When the chopper is ON, supply voltage VS is applied to the load .i.e. V0 = VS and inductor starts storing energy.
At this condition load current raises from Imin to Imax.
When the chopper is switched OFF, the supply voltage takes the path from L – D – Load – VS. During this period
the inductor discharges the stored e.m.f through diode D to the load. Thus the total voltage at the load V0 = VS +
Ldi/dt which s greater than the input voltage. Current changes from Imax to Imin.
86
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 48 - 55