Page 191 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 191
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
use these image sequences to learn about the development of weather patterns, forecast cyclones, monitor and
prevent wildfires and floods, and gather information on long-term issues like deforestation and coastline changes.
But because of their lower orbital altitude, SSO type of spacecraft can only cover a smaller region at once and
need more machines to do so continuously
Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) Satellites
The most frequent type of satellite transfer orbit is a geostationary one utilized to migrate from a transition orbit to
GEO. Spacecraft are not always placed directly into their ultimate orbit when propelled from Earth into space by
launch vehicles such as Falcon 9. Rockets carrying payload to GEO drop it off at transfer orbits, which are halfway
points on the path to its final position. Then a satellite’s engine fires to reach its destination orbit and adjust its
inclination . This shortcut allows the machine to reach geostationary orbit with minimal resources.
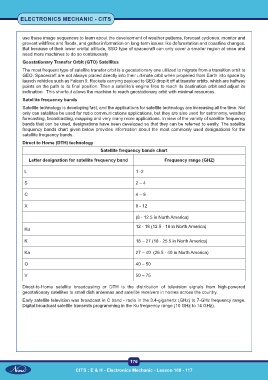
Satellite frequency bands
Satellite technology is developing fast, and the applications for satellite technology are increasing all the time. Not
only can satellites be used for radio communications applications, but they are also used for astronomy, weather
forecasting, broadcasting, mapping and very many more applications. In view of the variety of satellite frequency
bands that can be used, designations have been developed so that they can be referred to easily. The satellite
frequency bands chart given below provides information about the most commonly used designations for the
satellite frequency bands.
Direct to Home (DTH) technology
Satellite frequency bands chart
Letter designation for satellite frequency band Frequency range (GHZ)
L 1 -2
S 2 – 4
C 4 – 8
X 8 - 12
(8 - 12.5 in North America)
12 - 18 (12.5 - 18 in North America)
Ku
K 18 – 27 (18 - 25.5 in North America)
Ka 27 – 40 (26.5 - 40 in North America)
O 40 – 50
V 50 – 75
Direct-to-Home satellite broadcasting or DTH is the distribution of television signals from high-powered
geostationary satellites to small dish antennas and satellite receivers in homes across the country.
Early satellite television was broadcast in C band - radio in the 3.4-gigahertz (GHz) to 7-GHz frequency range.
Digital broadcast satellite transmits programming in the Ku frequency range (10 GHz to 14 GHz).
176
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 108 - 117