Page 319 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 319
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
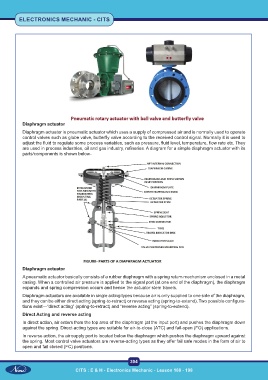
Diaphragm actuator
Diaphragm actuator is pneumatic actuator which uses a supply of compressed air and is normally used to operate
control valves such as globe valve, butterfly valve according to the received control signal. Normally it is used to
adjust the fluid to regulate some process variables, such as pressure, fluid level, temperature, flow rate etc. They
are used in process industries, oil and gas industry, refineries. A diagram for a simple diaphragm actuator with its
parts/components is shown below-
Diaphragm actuator
A pneumatic actuator basically consists of a rubber diaphragm with a spring return mechanism enclosed in a metal
casing. When a controlled air pressure is applied to the signal port (at one end of the diaphragm), the diaphragm
expands and spring compression occurs and hence the actuator stem travels.
Diaphragm actuators are available in single acting types because air is only supplied to one side of the diaphragm,
and they can be either direct acting (spring-to-retract) or reverse acting (spring-to-extend). Two possible configura-
tions exist—“direct acting” (spring-to-retract) and “reverse acting” (spring-to-extend).
Direct Acting and reverse acting
In direct action, air enters from the top area of the diaphragm (at the input port) and pushes the diaphragm down
against the spring. Direct-acting types are suitable for air-to-close (ATC) and fail-open (FO) applications.
In reverse action, the air supply port is located below the diaphragm which pushes the diaphragm upward against
the spring. Most control valve actuators are reverse-acting types as they offer fail safe modes in the form of air to
open and fail closed (FC) positions.
304
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 188 - 198