Page 329 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 329
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
MODULE 21 : Electrical control of AC/DC machines
& AC drives
LESSON 205 - 222 : Electrical control of AC/DC machines
Objectives
At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• state construction &b working priciple of AC/DC motors
• state the characteristics, advantages & disadvantages of the DC motors.
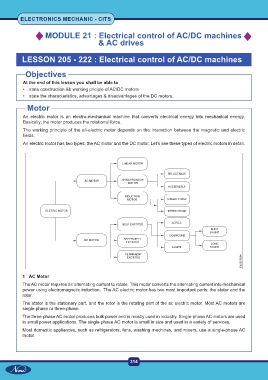
Motor
An electric motor is an electro-mechanical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Basically, the motor produces the rotational force.
The working principle of the all-electric motor depends on the interaction between the magnetic and electric
fields.
An electric motor has two types: the AC motor and the DC motor. Let’s see these types of electric motors in detail.
1 AC Motor
The AC motor requires an alternating current to rotate. This motor converts the alternating current into mechanical
power using electromagnetic induction. The AC electric motor has two most important parts: the stator and the
rotor.
The stator is the stationary part, and the rotor is the rotating part of the ac electric motor. Most AC motors are
single-phase or three-phase.
The three-phase AC motor produces bulk power and is mostly used in industry. Single-phase AC motors are used
in small power applications. The single-phase AC motor is small in size and used in a variety of services.
Most domestic appliances, such as refrigerators, fans, washing machines, and mixers, use a single-phase AC
motor.
314