Page 340 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 340
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
• Series
The field and armature winding on a series DC motor are connected to the power supply in a series. The same
current flows in the field and armature windings. A series wound motor can work with AC and DC voltage supply,
which makes it a universal motor. Series motors always rotate in the same direction regardless of the voltage
source. Their speed varies with the mechanical load.
• Compound
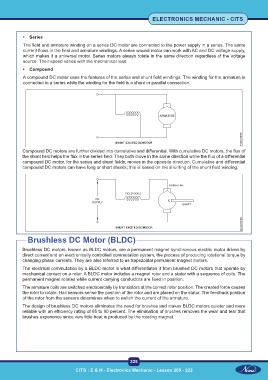
A compound DC motor uses the features of the series and shunt field windings. The winding for the armature is
connected in a series while the winding for the field is a shunt or parallel connection.
Compound DC motors are further divided into cumulative and differential. With cumulative DC motors, the flux of
the shunt field helps the flux in the series field. They both move in the same direction while the flux of a differential
compound DC motor, for the series and shunt fields, moves in the opposite direction. Cumulative and differential
compound DC motors can have long or short shunts; this is based on the shunting of the shunt field winding.
Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)
Brushless DC motors, known as BLDC motors, are a permanent magnet synchronous electric motor driven by
direct current and an electronically controlled commutation system, the process of producing rotational torque by
changing phase currents. They are also referred to as trapezoidal permanent magnet motors.
The electrical commutation by a BLDC motor is what differentiates it from brushed DC motors that operate by
mechanical contact on a rotor. A BLDC motor includes a magnet rotor and a stator with a sequence of coils. The
permanent magnet rotates while current carrying conductors are fixed in position.
The armature coils are switched electronically by transistors at the correct rotor position. The created force causes
the rotor to rotate. Hall sensors sense the position of the rotor and are placed on the stator. The feedback position
of the rotor from the sensors determines when to switch the current of the armature.
The design of brushless DC motors eliminates the need for brushes and makes BLDC motors quieter and more
reliable with an efficiency rating of 85 to 90 percent. The elimination of brushes removes the wear and tear that
brushes experience since very little heat is produced by the rotating magnet.
325
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 205 - 222