Page 347 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 347
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
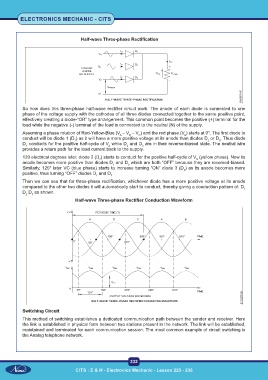
Half-wave Three-phase Rectification
So how does this three-phase half-wave rectifier circuit work. The anode of each diode is connected to one
phase of the voltage supply with the cathodes of all three diodes connected together to the same positive point,
effectively creating a diode-“OR” type arrangement. This common point becomes the positive (+) terminal for the
load while the negative (-) terminal of the load is connected to the neutral (N) of the supply.
Assuming a phase rotation of Red-Yellow-Blue (V – V – V ) and the red phase (V ) starts at 0°. The first diode to
B
A
C
A
conduct will be diode 1 (D ) as it will have a more positive voltage at its anode than diodes D or D . Thus diode
1
2
3
D conducts for the positive half-cycle of V while D and D are in their reverse-biased state. The neutral wire
3
1
A
2
provides a return path for the load current back to the supply.
120 electrical degrees later, diode 2 (D ) starts to conduct for the positive half-cycle of V (yellow phase). Now its
2
B
anode becomes more positive than diodes D and D which are both “OFF” because they are reversed-biased.
1
3
Similarly, 120° later VC (blue phase) starts to increase turning “ON” diode 3 (D ) as its anode becomes more
3
positive, thus turning “OFF” diodes D and D .
1 2
Then we can see that for three-phase rectification, whichever diode has a more positive voltage at its anode
compared to the other two diodes it will automatically start to conduct, thereby giving a conduction pattern of: D
1
D D as shown.
3
2
Half-wave Three-phase Rectifier Conduction Waveform
Switching Circuit
This method of switching establishes a dedicated communication path between the sender and receiver. Here
the link is established in physical form between two stations present in the network. The link will be established,
maintained and terminated for each communication session. The most common example of circuit switching is
the Analog telephone network.
332
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 223 - 236