Page 200 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 200
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
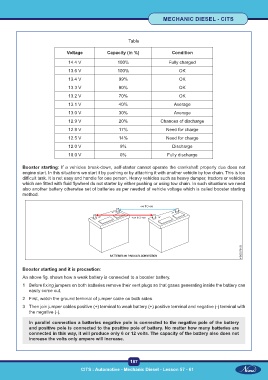
Table
Voltage Capacity (in %) Condition
14.4 V 100% Fully charged
13.6 V 100% OK
13.4 V 99% OK
13.3 V 90% OK
13.2 V 70% OK
13.1 V 40% Average
13.0 V 30% Average
12.9 V 20% Chances of discharge
12.8 V 17% Need for charge
12.5 V 14% Need for charge
12.0 V 9% Discharge
10.0 V 0% Fully discharge
Booster starting: If a vehicles break-down, self-starter cannot operate the crankshaft properly due does not
engine start. In this situations we start it by pushing or by attaching it with another vehicle by tow chain. This is too
difficult task. It is not easy and handle for one person. Heavy vehicles such as heavy dumper, tractors or vehicles
which are fitted with fluid flywheel do not starter by either pushing or using tow chain. In such situations we need
also another battery otherwise set of batteries as per needed of vehicle voltage which is called booster starting
method.
Booster starting and it is precaution:
An above fig. shows how a weak battery is connected to a booster battery.
1 Before fixing jumpers on both batteries remove their vent plugs so that gases generating inside the battery can
easily come out.
2 First, watch the ground terminal of jumper cable on both sides.
3 Then join jumper cables positive (+) terminal to weak battery (+) positive terminal and negative (-) terminal with
the negative (-).
In parallel connection a batteries negative pole is connected to the negative pole of the battery
and positive pole is connected to the positive pole of battery. No matter how many batteries are
connected in this way, it will produce only 6 or 12 volts. The capacity of the battery also does not
increase the volts only ampere will increase.
187
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 57 - 61