Page 257 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 257
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
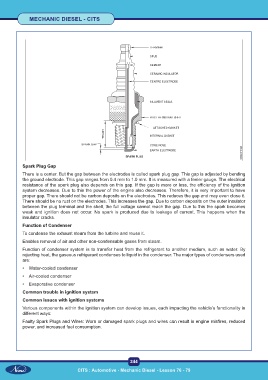
Spark Plug Gap
There is a center. But the gap between the electrodes is called spark plug gap. This gap is adjusted by bending
the ground electrode. This gap ranges from 0.4 mm to 1.0 mm. It is measured with a feeler gauge. The electrical
resistance of the spark plug also depends on this gap. If the gap is more or less, the efficiency of the ignition
system decreases. Due to this the power of the engine also decreases. Therefore, it is very important to have
proper gap. There should not be carbon deposits on the electrodes. This reduces the gap and may even close it.
There should be no rust on the electrodes. This increases the gap. Due to carbon deposits on the outer insulator
between the plug terminal and the shell, the full voltage cannot reach the gap. Due to this the spark becomes
weak and ignition does not occur. No spark is produced due to leakage of current. This happens when the
insulator cracks.
Function of Condenser
To condense the exhaust steam from the turbine and reuse it.
Enables removal of air and other non-condensable gases from steam.
Function of condenser system is to transfer heat from the refrigerant to another medium, such as water. By
rejecting heat, the gaseous refrigerant condenses to liquid in the condenser. The major types of condensers used
are:
• Water-cooled condenser
• Air-cooled condenser
• Evaporative condenser
Common trouble in ignition system
Common issues with ignition systems
Various components within the ignition system can develop issues, each impacting the vehicle’s functionality in
different ways:
Faulty Spark Plugs and Wires: Worn or damaged spark plugs and wires can result in engine misfires, reduced
power, and increased fuel consumption.
244
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 76 - 79