Page 53 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 53
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
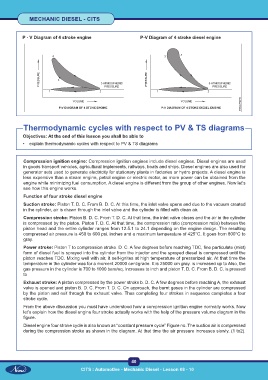
P - V Diagram of 4 stroke engine P-V Diagram of 4 stroke diesel engine
Thermodynamic cycles with respect to PV & TS diagrams
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• explain thermodynamic cycles with respect to PV & TS diagrams
Compression ignition engine: Compression ignition engines include diesel engines. Diesel engines are used
in goods transport vehicles, agricultural implements, railways, boats and ships. Diesel engines are also used for
generator sets used to generate electricity for stationary plants in factories or hydro projects. A diesel engine is
less expensive than a steam engine, petrol engine or electric motor, as more power can be obtained from the
engine while minimizing fuel consumption. A diesel engine is different from the group of other engines. Now let’s
see how this engine works.
Function of four stroke diesel engine
Suction stroke: Piston T. D. C. From B. D. C. At this time, the inlet valve opens and due to the vacuum created
in the cylinder, air is drawn through the inlet valve and the cylinder is filled with clean air.
Compression stroke: Piston B. D. C. From T. D. C. At that time, the inlet valve closes and the air in the cylinder
is compressed by the piston. Piston T. D. C. At that time, the compression ratio (compression ratio) between the
piston head and the entire cylinder ranges from 12.5.1 to 24.1 depending on the engine design. The resulting
compressed air pressure is 450 to 600 psi. inches and a maximum temperature of 425°C. It goes from 800°C to
gray.
Power stroke: Piston T to compression stroke. D. C. A few degrees before reaching TDC, fine particulate (mist)
form of diesel fuel is sprayed into the cylinder from the injector and the sprayed diesel is compressed until the
piston reaches TDC. Mixing well with air, it self-ignites at high temperature of pressurized air. At that time the
temperature in the cylinder was for a moment 20000 centigrade. It is 25000 cm gray. is increased up to Also, the
gas pressure in the cylinder is 700 to 1000 bara/sq. Increases to inch and piston T. D. C. From B. D. C. is pressed
to
Exhaust stroke: A piston compressed by the power stroke b. D. C. A few degrees before reaching A, the exhaust
valve is opened and piston B. D. C. From T. D. C. On approach, the burnt gases in the cylinder are compressed
by the piston and exit through the exhaust valve. Thus completing four strokes in sequence completes a four
stroke cycle.
From the above discussion you must have understood how a compression ignition engine normally works. Now
let’s explain how the diesel engine four stroke actually works with the help of the pressure volume diagram in the
figure.
Diesel engine four stroke cycle is also known as “constant pressure cycle” Figure no. The suction air is compressed
during the compression stroke as shown in the diagram. At that time the air pressure increases slowly. (1 to2).
40
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 08 - 10