Page 14 - WCS - Electrical
P. 14
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
EXERCISE 1 : Fraction
Unit, Fractions - Fractions - Addition, subtraction,
multiplication & division
Description
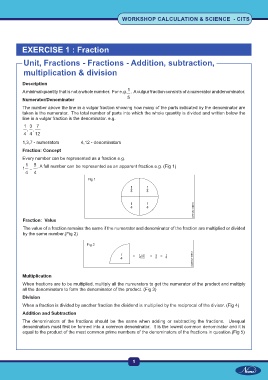
1
A minimal quantity that is not a whole number. For e.g. . A vulgur fraction consists of a numerator anddenominator.
Numerator/Denominator 5
The number above the line in a vulgar fraction showing how many of the parts indicated by the denominator are
taken is the numerator. The total number of parts into which the whole quantity is divided and written below the
line in a vulgar fraction is the denominator. e.g.
1 , 3 , 7
4 4 12
1,3,7 - numerators 4,12 - denominators
Fraction: Concept
Every number can be represented as a fraction.e.g.
5
1 1 = , A full number can be represented as an apparent fraction.e.g. (Fig 1)
4 4
Fraction: Value
The value of a fraction remains the same if the numerator and denominator of the fraction are multiplied or divided
by the same number.(Fig 2)
Multiplication
When fractions are to be multiplied, multiply all the numerators to get the numerator of the product and multiply
all the denominators to form the denominator of the product. (Fig 3)
Division
When a fraction is divided by another fraction the dividend is multiplied by the reciprocal of the divisor. (Fig 4)
Addition and Subtraction
The denominators of the fractions should be the same when adding or subtracting the fractions. Unequal
denominators must first be formed into a common denominator. It is the lowest common denominator and it is
equal to the product of the most common prime numbers of the denominators of the fractions in question.(Fig 5)
1