Page 187 - WCS - Electrical
P. 187
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
What is a Molecule?
molecule-imgA molecule is the smallest unit of a chemical compound and it exhibits the same chemical properties
of that specific compound. As molecules are made up of atoms jointly held by chemical bonds, they can vary
greatly in terms of complexity and size. The oxygen we breathe has a molecular formula O . Should we consider
2
this as an element or compound? When two or more atoms of the same elements combine together, we call them
Molecules. So, we call O as an oxygen molecule. In the same way, we find hydrogen molecules H , chlorine
2
2
molecules Cl and others in nature.
2
Types of electric current
• Direct current
• Alternating current
Direct current
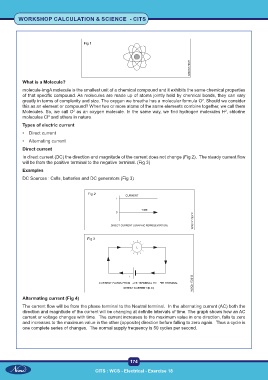
In direct current (DC) the direction and magnitude of the current does not change (Fig 2). The steady current flow
will be from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. (Fig 3)
Examples
DC Sources : Cells, batteries and DC generators (Fig 3)
Altermating current (Fig 4)
The current flow will be from the phase terminal to the Neutral terminal. In the alternating current (AC) both the
direction and magnitude of the current will be changing at definite intervals of time. The graph shows how an AC
current or voltage changes with time. The current increases to the maximum value in one direction, falls to zero
and increases to the maximum value in the other (opposite) direction before falling to zero again. Thus a cycle is
one complete series of changes. The normal supply frequency is 50 cycles per second.
174
CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 18