Page 204 - WCS - Electrical
P. 204
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
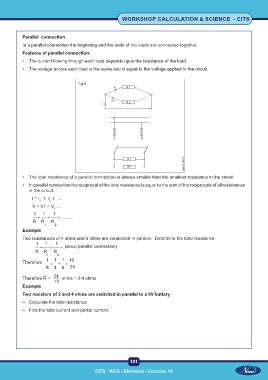
Parallel connection
In a parallel connection the beginning and the ends of the loads are connected together.
Example
Features of parallel connection: Example
Two resistors of 2 and 4 ohms are switched in parallel
Example
Two resistors of 2 and 4 ohms are switched in parallel
• The current flowing through each load depends upon the resistance of the load.
to a 6V battery
to a 6V battery
Two resistors of 2 and 4 ohms are switched in parallel
• The voltage across each load is the same and is equal to the voltage applied to the circuit.
– Calculate the total resistance
to a 6V battery
Example
– Calculate the total resistance
– Find the total current and partial current.
– Calculate the total resistance
Two resistors of 2 and 4 ohms are switched in parallel
– Find the total current and partial current.
to a 6V battery
– Find the total current and partial current.
– Calculate the total resistance
– Find the total current and partial current.
Solution
Solution
Solution
Total resistance
The total resistance of a parallel connection is always
• • The total resistance of a parallel connection is always Total resistance
smaller than the smallest resistance in the circuit.
smaller than the smallest resistance in the circuit. 1 1 Total resistance
The total resistance of a parallel connection is always
•
1
1
Solution 1
=
1 +
In parallel connection the reciprocal of the total
smaller than the smallest resistance in the circuit.
• • In parallel connection the reciprocal of the total R R tot tot = R 1 + R R 1 2 2 1
1 R
resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of all
1
+
=
In parallel connection the reciprocal of the total
1
1
•
2
+
1
• resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of all = Total resistance
The total resistance of a parallel connection is always
R
tot +2
R 1
resistances in the circuit.
1 +
R 1 =
resistances in the circuit. 2 2 + 4 4 = 1 1 1 4 4 1 1 2 + 1 2
resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of all =
smaller than the smallest resistance in the circuit.
1
= l + l + ...
l
resistances in the circuit.
+
=
=
3
= l + l + ...
l
+
1
2
= Ω
3
=
•
In parallel connection the reciprocal of the total
4
4
2
2
1
• The total resistance of a parallel connection is always smaller than the smallest resistance in the circuit.
R
R Ω
R
=
V = V = V ...
= l + l + ...
resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of all
V = V = V ... 1 2 4 tot 4 3 1 2
2
l 1
2 Ω
+
1
1 1
1 =4
• In parallel connection the reciprocal of the total resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of all resistances
2
1
resistances in the circuit.
Ω
+ 4 =
= R
= 1 1=
in the circuit. 111 V = V = V ... R tot tot 2 = 4 1= 4 4 3 Ω
3
1
2
1
1
3
l 1 3 R = 4 3 = 1 1 Ω
= l + l + ... ..........
2 ..........
1
R
R
R R 1 R 1 .......... I Total = I + I current
Ω tot
=
l = l + l + ... 111
3
3
V = V = V ...
4
2 R 2
1
2
1 1
V = V1 = V ... RRR 2 2 I Total = I + I current
2
1
4
1
2
Ω + I current
Example
= U
R
1
=
Example 1 1 2 But tot I 1 I Total = I 6V = 2 3A
3A
U
=
=
6V =
1
1
But
1
3
I
1
3 =
2Ω
= R
..........
Two resistances of 4 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in
Example
Two resistances of 4 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in But R 1 I 1 1 = U 2Ω = 6V = 3A
R
R
R
parallel. Determine the total resistance.
U
R 6V
2Ω
1
2
parallel. Determine the total resistance. I Total = I + I current
U
1 6V
Two resistances of 4 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in
=
=
2 1
1.5A
=
I
2
4Ω
Example I 2 = R 2 = 4Ω = 1.5A
parallel. Determine the total resistance.
R
Example 1 2 U U 6V 6V
1
1
= =
3A 1.5A=
= =
But
=
1
1
1
I I
2
1 3 = l
tota
R R 1.5A +A
Two resistances of 4 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in parallel. Determine the total resistance.
2Ω 4Ω
I
(since parallel connection)
Two resistances of 4 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in I total 3A = 11.5A + 2
R
R
R
1 (since parallel connection)
1
1
R
4.5=
3A = Amp
(since parallel connection)
R 1
6V 1.5A +
R 2
parallel. Determine the total resistance. I total Amp
U
4.5=
2
1
R R R (since parallel connection) I 2 = R = 4Ω = 1.5A
2
1 2 4.5= Amp
Assume the given resistors in the assignment
10
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 I Assume the given resistors in the assignment
+
total
3A =
1.5A
Therefore
Therefore
as bulb with filaments and other current con-
Therefore R R (since parallel connection) as bulb with filaments and other current con-
24
4
6
R
R
1
1
Assume the given resistors in the assignment
10
1 24
6
R
suming devices like Horn, Wiper etc of the
4.5=
Amp
2
1
Therefore 4 R as bulb with filaments and other current con-
suming devices like Horn, Wiper etc of the
24
6
4
vehicle.
24
suming devices like Horn, Wiper etc of the
Therefore R = ohms = 2.4 ohms vehicle.
ohms = 2.4 ohms
24
Therefore R
1
ohms
Therefore R 1 10 1 ohms = 2.4 Assume the given resistors in the assignment
10
vehicle.
10
24
Therefore
Example R as bulb with filaments and other current con-
ohms = 2.4 ohms
24
Therefore R
4
6
10
suming devices like Horn, Wiper etc of the
Two resistors of 2 and 4 ohms are switched in parallel to a 6V battery
Assignment
24
Assignment vehicle.
ohms = 2.4 ohms
Therefore R
– Calculate the total resistance
10
Assignment
– Find the total current and partial current.
= 6 Volts
= 40 Ohms
1 1 R R = 40 Ohms 2 2 V V = 6 Volts
Assignment I I R = 6.5 Amps 2 I I V = 0.5 Amps
= 6 Volts
= 0.5 Amps
= 40 Ohms
1
= 6.5 Amps
= ______ Ohms
= 0.5 Amps
= ______ Volts
= 6.5 Amps
V V I = ______ Volts R R I = ______ Ohms
= ______ Ohms
1 R V = 40 Ohms 2 V R = 6 Volts
= ______ Volts
I = 6.5 Amps I = 0.5 Amps
V = ______ Volts R = ______ Ohms
191
CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 18
Workshop Calculation & Science : (NSQF) Exercise 1.7.35
109
Workshop Calculation & Science : (NSQF) Exercise 1.7.35 109
Workshop Calculation & Science : (NSQF) Exercise 1.7.35 109
Workshop Calculation & Science : (NSQF) Exercise 1.7.35 109