Page 216 - WCS - Electrical
P. 216
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
Atmospheric Pressure
The Atmospheric air exerts a normal pressure upon all the surfaces with which it comes in contact, is called as
atmospheric pressure.
The atmospheric pressure varies with the altitude and it can be measured by means of a barometer.It is also
called as barometric pressure.
There are two types of barometers ie. Mercury barometer and Aneroid barometer.
At sea level, under normal atmospheric condition at 15°C, the equivalent values of atmospheric pressure are
101325 N/m2 or 10.33m of water or 76 cm of mercury.
1 atm = 10.33 m of water=1.01325 bar
P= γ.h=9.81x10.33=101.325 kN/m² or kPa
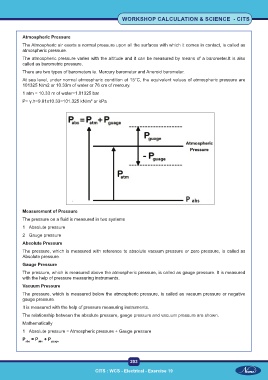
Measurement of Pressure
The pressure on a fluid is measured in two systems
1 Absolute pressure
2 Gauge pressure
Absolute Pressure
The pressure, which is measured with reference to absolute vacuum pressure or zero pressure, is called as
Absolute pressure.
Gauge Pressure
The pressure, which is measured above the atmospheric pressure, is called as gauge pressure. It is measured
with the help of pressure measuring instruments.
Vacuum Pressure
The pressure, which is measured below the atmospheric pressure, is called as vacuum pressure or negative
gauge pressure.
It is measured with the help of pressure measuring instruments.
The relationship between the absolute pressure, gauge pressure and vacuum pressure are shown.
Mathematically
1 Absolute pressure = Atmospheric pressure + Gauge pressure
P abs = P atm + P guage
203
CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 19