Page 111 - CITS - WCS - Mechanical
P. 111
WORKSHOP SCIENCE - CITS
Specific weight: In fluid mechanics, specific weight represents the force exerted by gravity on a unit volume of
a fluid. For this reason, units are expressed as force per unit volume (e.g., N/m3 or lbf/ft3). Specific weight can
be used as a characteristic property of a fluid. To find the specific weight of an unknown fluid using a manometer,
The specific weight can then be calculated using the formula: specific weight = pressure/density. The SI unit for
specific weight is [N/m3]. The imperial unit is [lb/ft3].
Specific volume: Specific volume is a property of materials, defined as the number of cubic meters occupied by
one kilogram of a particular substance. The standard unit is the meter cubed per kilogram (m3/kg or m3·kg−1).
There are three common formulas used to calculate specific volume (ν): v= V/m where V is volume and m is
mass. ν = 1 /ρ = ρ-1 where ρ is density. ν = RT / PM = RT / P where R is the ideal gas constant, T is temperature,
P is pressure, and M is the molarity.
Specific Gravity: The specific gravity of a liquid is the relative weight that liquid compare to an equal volume of
water. The specific gravity of water is de facto 1. Liquids that are lighter than water have a specific gravity less
than 1 and those heavier than water have a specific gravity greater than 1.
Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees Celsius.
The ratio of the density of a substance to the density of some substance (as pure water) taken as a standard
when both densities are obtained by weighing in air. Since specific gravity is a ratio, so it has no units.
Concept of Atmospheric Pressure: That pressure is called atmospheric pressure, or air pressure. It is the
force exerted on a surface by the air above it as gravity pulls it to Earth. Atmospheric pressure is commonly
measured with a barometer. In a barometer, a column of mercury in a glass tube rises or falls as the weight of the
atmosphere changes. The SI unit of atmospheric pressure is Pascal (Pa). Another unit of atmospheric pressure
is atm and 1 atm = 101325 Pa.
Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the air around us while Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by
the atmospheric on the earth. Air pressure is measured by tore gauge while atmospheric pressure is measured
using mercury barometer. Where the air pressure is assumed to be zero, is called the Kármán line, which is
located 100 km (62 mi) up.
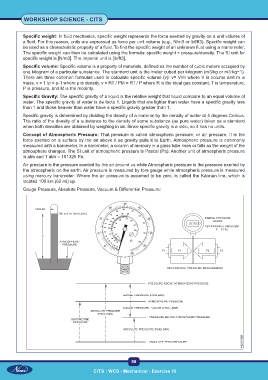
Gauge Pressure, Absolute Pressure, Vacuum & Differential Pressure:
98
CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 10