Page 143 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 143
WELDER - CITS
In the case of joints which are not free to expand i.e., restrained joints and in joints in which there is a stress
already present before welding, the residual stresses will be more after cooling of the joint. If these residual
stresses are not removed after welding, then the joint will fail or distort when they are put into use or the joint is
machined or the joint is subjected to dynamic loading.
To avoid the above problems a welded job is usually either normalised or annealed or stress-relieve
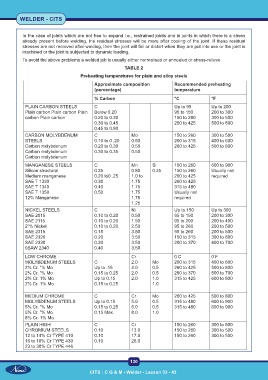
TABLE 2
Preheating temperatures for plain and alloy steels
Approximate composition Recommended preheating
(percentage) temperature
% Carbon °C °F
PLAIN CARBON STEELS C Up to 95 Up to 200
Plain carbon Plain carbon Plain Below 0.20 95 to 150 200 to 300
carbon Plain carbon 0.20 to 0.30 150 to 280 300 to 500
0.30 to 0.45 260 to 425 500 to 800
0.45 to 0.80
CARBON MOLYBDENUM C Mo 150 to 260 300 to 500
STEELS 0.10 to 0 .20 0.50 200 to 315 400 to 600
Carbon molybdenum 0.20 to 0.30 0.50 260 to 425 500 to 800
Carbon molybdenum 0.30 to 0.35 0.50
Carbon molybdenum
MANGANESE STEELS C Mn Si 150 to 260 600 to 900
Silicon structural 0.35 0.80 0.25 150 to 260 Usually not
Medium manganese 0.20 to0 .25 1.0 to 200 to 425 required
SAE T 1330 0.30 1.75 260 to 425
SAE T 1340 0.40 1.75 315 to 480
SAE T 1350 0.50 1.75 Usually not
12% Manganese 1.75 required
1.25
NICKEL STEELS C Ni Up to 150 Up to 300
SAE 2015 0.10 to 0.20 0.50 95 to 150 200 to 300
SAE 2115 0.10 to 0.20 1.50 95 to 200 200 to 400
2”% Nickel 0.10 to 0.20 2.50 95 to 260 200 to 500
SAE 2315 0.15 3.50 95 to 260 200 to 500
SAE 2320 0.20 3.50 150 to 315 300 to 600
SAE 2330 0.30 3.50 200 to 370 400 to 700
0SAW 2340 0.40 3.50
LOW CHROME Cr 0 C 0 F
MOLYBDENUM STEELS C 2.0 Mo 200 to 315 400 to 600
2% Cr. ”% Mo Up to .15 2.0 0.5 260 to 425 500 to 800
2% Cr. ”% Mo 0.15 to 0.25 2.0 0.5 260 to 370 500 to 700
2% Cr. 1% Mo Up to 0.15 2.0 1.0 315 to 425 600 to 800
2% Cr. 1% Mo 0.15 to 0.25 1.0
MEDIUM CHROME C Cr Mo 260 to 425 500 to 800
MOLYBDENUM STEELS Up to 0.15 5.0 0.5 315 to 480 600 to 900
5% Cr. ”% Mo 0.15 to 0.25 5.0 0.5 315 to 480 600 to 900
5% Cr. ”% Mo 0.15 Max. 8.0 1.0
8% Cr. 1% Mo
PLAIN HIGH C Cr 150 to 260 300 to 500
CHROMIUM STEELS 0.10 13.0 150 to 260 300 to 500
12 to 14% Cr TYPE 410 0.10 17.0 150 to 260 300 to 500
16 to 18% Cr TYPE 430 0.10 26.0
23 to 30% Cr TYPE 446
130
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 33 - 43 CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 33 - 43