Page 24 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 24
WELDER - CITS
Lesson 4&5 : Introduction of Arc, Gas and another
welding process and their application
Objectives
At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• explain the function arc welding definition, application
• explain the function gas welding definition, application
• explain the function MIG welding definition, application
• explain the function TIG welding definition, application
• explain the function Submerged arc welding definition, application.
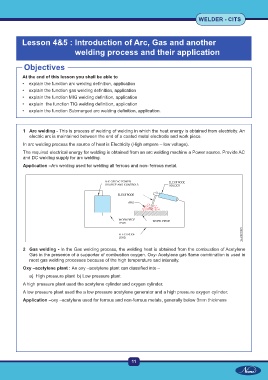
1 Arc welding - This is process of welding of welding in which the heat energy is obtained from electricity. An
electric arc is maintained between the end of a coated metal electrode and work piece.
In arc welding process the source of heat is Electricity (High ampere – low voltage).
The required electrical energy for welding is obtained from an arc welding machine a Power source. Provide AC
and DC welding supply for arc welding.
Application –Arc welding used for welding all ferrous and non- ferrous metal.
2 Gas welding - In the Gas welding process, the welding heat is obtained from the combustion of Acetylene
Gas in the presence of a supporter of combustion oxygen. Oxy- Acetylene gas flame combination is used in
most gas welding processes because of the high temperature and intensity.
Oxy –acetylene plant : An oxy –acetylene plant can classified into –
a) High pressure plant b) Low pressure plant.
A high pressure plant used the acetylene cylinder and oxygen cylinder.
A low pressure plant used the a low pressure acetylene generator and a high pressure oxygen cylinder.
Application –oxy –acetylene used for ferrous and non-ferrous metals, generally below 3mm thickness
11
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 1-3