Page 15 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 15
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
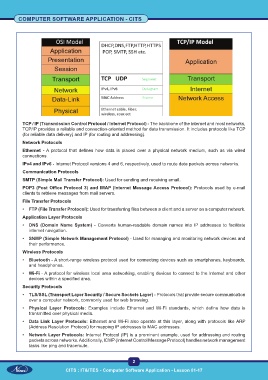
TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) - The backbone of the internet and most networks,
TCP/IP provides a reliable and connection-oriented method for data transmission. It includes protocols like TCP
(for reliable data delivery) and IP (for routing and addressing).
Network Protocols
Ethernet - A protocol that defines how data is placed over a physical network medium, such as via wired
connections.
IPv4 and IPv6 - Internet Protocol versions 4 and 6, respectively, used to route data packets across networks.
Communication Protocols
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Used for sending and receiving email.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Protocols used by e-mail
clients to retrieve messages from mail servers.
File Transfer Protocols
• FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Used for transferring files between a client and a server on a computer network.
Application Layer Protocols
• DNS (Domain Name System) - Converts human-readable domain names into IP addresses to facilitate
internet navigation.
• SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) - Used for managing and monitoring network devices and
their performance.
Wireless Protocols
• Bluetooth - A short-range wireless protocol used for connecting devices such as smartphones, keyboards,
and headphones.
• Wi-Fi - A protocol for wireless local area networking, enabling devices to connect to the Internet and other
devices within a specified area.
Security Protocols
• TLS/SSL (Transport Layer Security / Secure Sockets Layer) - Protocols that provide secure communication
over a computer network, commonly used for web browsing.
• Physical Layer Protocols: Examples include Ethernet and Wi-Fi standards, which define how data is
transmitted over physical media.
• Data Link Layer Protocols: Ethernet and Wi-Fi also operate at this layer, along with protocols like ARP
(Address Resolution Protocol) for mapping IP addresses to MAC addresses.
• Network Layer Protocols: Internet Protocol (IP) is a prominent example, used for addressing and routing
packets across networks. Additionally, ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) handles network management
tasks like ping and traceroute.
2
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 01-17