Page 19 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 19
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
Network Topology
A topological space is a set endowed with a structure, called a topology, that allows defining continuous deformation
of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces,
are examples of a topological space, as any distance or metric defines a topology.
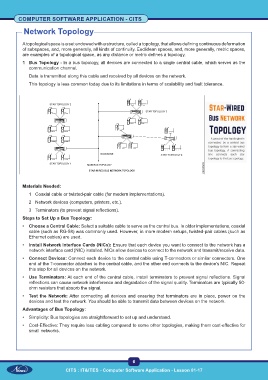
1 Bus Topology - In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single central cable, which serves as the
communication channel.
Data is transmitted along this cable and received by all devices on the network.
This topology is less common today due to its limitations in terms of scalability and fault tolerance.
Materials Needed:
1 Coaxial cable or twisted-pair cable (for modern implementations).
2 Network devices (computers, printers, etc.).
3 Terminators (to prevent signal reflections).
Steps to Set Up a Bus Topology:
• Choose a Central Cable: Select a suitable cable to serve as the central bus. In older implementations, coaxial
cable (such as RG-58) was commonly used. However, in more modern setups, twisted-pair cables (such as
Ethernet cables) are used.
• Install Network Interface Cards (NICs): Ensure that each device you want to connect to the network has a
network interface card (NIC) installed. NICs allow devices to connect to the network and transmit/receive data.
• Connect Devices: Connect each device to the central cable using T-connectors or similar connectors. One
end of the T-connector attaches to the central cable, and the other end connects to the device’s NIC. Repeat
this step for all devices on the network.
• Use Terminators: At each end of the central cable, install terminators to prevent signal reflections. Signal
reflections can cause network interference and degradation of the signal quality. Terminators are typically 50-
ohm resistors that absorb the signal.
• Test the Network: After connecting all devices and ensuring that terminators are in place, power on the
devices and test the network. You should be able to transmit data between devices on the network.
Advantages of Bus Topology:
• Simplicity: Bus topologies are straightforward to set up and understand.
• Cost-Effective: They require less cabling compared to some other topologies, making them cost-effective for
small networks.
6
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 01-17