Page 378 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 378
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
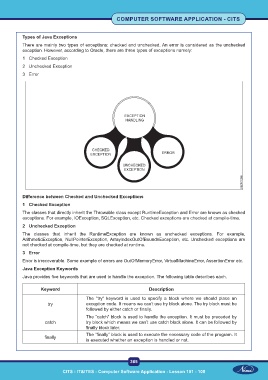
Types of Java Exceptions
There are mainly two types of exceptions: checked and unchecked. An error is considered as the unchecked
exception. However, according to Oracle, there are three types of exceptions namely:
1 Checked Exception
2 Unchecked Exception
3 Error
Difference between Checked and Unchecked Exceptions
1 Checked Exception
The classes that directly inherit the Throwable class except RuntimeException and Error are known as checked
exceptions. For example, IOException, SQLException, etc. Checked exceptions are checked at compile-time.
2 Unchecked Exception
The classes that inherit the RuntimeException are known as unchecked exceptions. For example,
ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, etc. Unchecked exceptions are
not checked at compile-time, but they are checked at runtime.
3 Error
Error is irrecoverable. Some example of errors are OutOfMemoryError, VirtualMachineError, AssertionError etc.
Java Exception Keywords
Java provides five keywords that are used to handle the exception. The following table describes each.
Keyword Description
The "try" keyword is used to specify a block where we should place an
try exception code. It means we can't use try block alone. The try block must be
followed by either catch or finally.
The “catch” block is used to handle the exception. It must be preceded by
catch try block which means we can’t use catch block alone. It can be followed by
finally block later.
The “finally” block is used to execute the necessary code of the program. It
finally
is executed whether an exception is handled or not.
365
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 101 - 108 CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 101 - 108