Page 380 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 380
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
1 int a[]=new int[5];
2 a[10]=50; //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Types of Exception in Java
In Java, exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a program and disrupts the normal flow of the
program’s instructions. Bugs or errors that we don’t want and restrict our program’s normal execution of code are
referred to as exceptions. In this section, we will focus on the types of exceptions in Java and the differences
between the two.
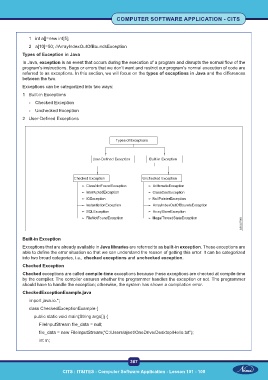
Exceptions can be categorized into two ways:
1 Built-in Exceptions
- Checked Exception
- Unchecked Exception
2 User-Defined Exceptions
Built-in Exception
Exceptions that are already available in Java libraries are referred to as built-in exception. These exceptions are
able to define the error situation so that we can understand the reason of getting this error. It can be categorized
into two broad categories, i.e., checked exceptions and unchecked exception.
Checked Exception
Checked exceptions are called compile-time exceptions because these exceptions are checked at compile-time
by the compiler. The compiler ensures whether the programmer handles the exception or not. The programmer
should have to handle the exception; otherwise, the system has shown a compilation error.
CheckedExceptionExample.java
import java.io.*;
class CheckedExceptionExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
FileInputStream file_data = null;
file_data = new FileInputStream(“C:/Users/ajeet/OneDrive/Desktop/Hello.txt”);
int m;
367
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 101 - 108 CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 101 - 108