Page 384 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 384
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
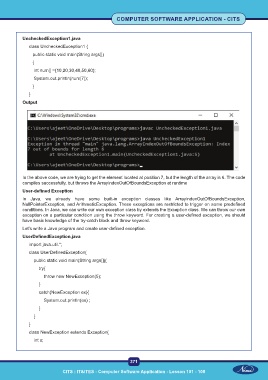
UncheckedException1.java
class UncheckedException1 {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int num[] ={10,20,30,40,50,60};
System.out.println(num[7]);
}
}
Output
In the above code, we are trying to get the element located at position 7, but the length of the array is 6. The code
compiles successfully, but throws the ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException at runtime
User-defined Exception
In Java, we already have some built-in exception classes like ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,
NullPointerException, and ArithmeticException. These exceptions are restricted to trigger on some predefined
conditions. In Java, we can write our own exception class by extends the Exception class. We can throw our own
exception on a particular condition using the throw keyword. For creating a user-defined exception, we should
have basic knowledge of the try-catch block and throw keyword.
Let’s write a Java program and create user-defined exception.
UserDefinedException.java
import java.util.*;
class UserDefinedException{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
throw new NewException(5);
}
catch(NewException ex){
System.out.println(ex) ;
}
}
}
class NewException extends Exception{
int x;
371
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 101 - 108 CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 101 - 108