Page 133 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 133
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
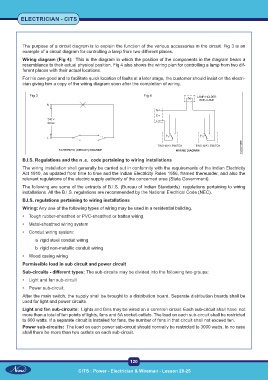
The purpose of a circuit diagram is to explain the function of the various accessories in the circuit. Fig 3 is an
example of a circuit diagram for controlling a lamp from two different places.
Wiring diagram (Fig 4): This is the diagram in which the position of the components in the diagram bears a
resemblance to their actual physical position. Fig 4 also shows the wiring plan for controlling a lamp from two dif-
ferent places with their actual locations.
For his own good and to facilitate quick location of faults at a later stage, the customer should insist on the electri-
cian giving him a copy of the wiring diagram soon after the completion of wiring.
Fig 3 Fig 4
B.I.S. Regulations and the n .e. code pertaining to wiring installations
The wiring installation shell generally be carried out in conformity with the requirements of the Indian Electricity
Act 1910, as updated from time to time and the Indian Electricity Rules 1956, framed thereunder, and also the
relevant regulations of the electric supply authority of the concerned area (State Government).
The following are some of the extracts of B.I.S. (Bureau of Indian Standards) regulations pertaining to wiring
installations. All the B.I.S. regulations are recommended by the National Electrical Code (NEC).
B.I.S. regulations pertaining to wiring installations
Wiring: Any one of the following types of wiring may be used in a residential building.
• Tough rubber-sheathed or PVC-sheathed or batten wiring.
• Metal-sheathed wiring system
• Conduit wiring system:
a rigid steel conduit wiring
b rigid non-metallic conduit wiring
• Wood casing wiring
Permissible load in sub circuit and power circuit
Sub-circuits - different types: The sub-circuits may be divided into the following two groups:
• Light and fan sub-circuit
• Power sub-circuit.
After the main switch, the supply shall be brought to a distribution board. Separate distribution boards shall be
used for light and power circuits.
Light and fan sub-circuits: Lights and fans may be wired on a common circuit. Each sub-circuit shall have not
more than a total of ten points of lights, fans and 6A socket-outlets. The load on each sub-circuit shall be restricted
to 800 watts. If a separate circuit is installed for fans, the number of fans in that circuit shall not exceed ten.
Power sub-circuits: The load on each power sub-circuit should normally be restricted to 3000 watts. In no case
shall there be more than two outlets on each sub-circuit.
120
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 20-25