Page 137 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 137
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
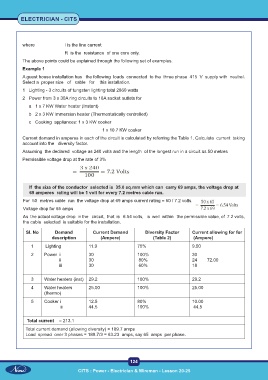
where I is the line current
R is the resistance of one core only.
The above points could be explained through the following set of examples.
Example 1
A guest house installation has the following loads connected to the three phase 415 V supply with neutral.
Select a proper size of cable for this installation.
1 Lighting - 3 circuits of tungsten lighting total 2860 watts
2 Power from 3 x 30A ring circuits to 16A socket outlets for
a 1 x 7 KW Water heater (Instant)
b 2 x 3 KW Immersion heater (Thermostatically controlled)
c Cooking appliances: 1 x 3 KW cooker
1 x 10.7 KW cooker
Current demand in amperes in each of the circuit is calculated by referring the Table 1. Calculate current taking
account into the diversity factor.
Assuming the declared voltage as 240 volts and the length of the longest run in a circuit as 50 metres
Permissible voltage drop at the rate of 3%
If the size of the conductor selected is 35.0 sq.mm which can carry 69 amps, the voltage drop at
69 amperes rating will be 1 volt for every 7.2 metres cable run.
For 50 metres cable run the voltage drop at 69 amps current rating = 50 / 7.2 volts.
Voltage drop for 65 amps
As the actual voltage drop in the circuit, that is 6.54 volts, is well within the permissible value, of 7.2 volts,
the cable selected is suitable for the installation.
SI. No Demand Current Demand Diversity Factor Current allowing for for
description (Ampere) (Table 2) (Ampere)
1 Lighting 11.9 75% 9.00
2 Power i 30 100% 30
ii 30 80% 24 72.00
iii 30 60% 18
3 Water heaters (inst) 29.2 100% 29.2
4 Water heaters 25.00 100% 25.00
(thermo)
5 Cooker i 12.5 80% 10.00
ii 44.5 100% 44.5
Total current = 213.1
Total current demand (allowing diversity) = 189.7 amps
Load spread over 3 phases = 189.7/3 = 63.23 amps, say 65 amps per phase.
124
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 20-25