Page 142 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 142
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
3 Connecting a number of earth electrodes in parallel reduces the earth electrode resistance.
4 Soldering the earth connections or using non-ferrous clamps lowers the earth electrode resistance.
5 Avoiding rust in the earth electrode connections lowers the earth electrode resistance.
Insulation resistance tester (Megger)
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to:
• state the working principle of an insulation tester (Megger)
• explain the construction and working of megger
• state the uses of an insulation tester like insulation test, continuity test etc.
• state the safety precautions to be observed while using an insulation tester.
Megger
It is an electrical measuring instrument generally used to measure the insulation resistance of an installation/
equipment etc in terms of Megaohms.
Necessity of megohmmeter
Ordinary ohmmeters and resistance bridges are not generally designed to measure extremely high values of
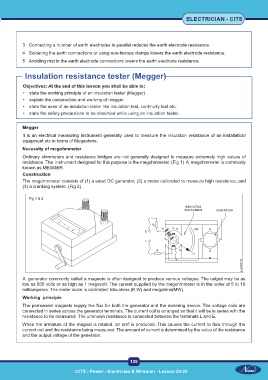
resistance. The instrument designed for this purpose is the megohmmeter. (Fig 1) A megohmmeter is commonly
known as MEGGER.
Construction
The megohmmeter consists of (1) a small DC generator, (2) a meter calibrated to measure high resistance, and
(3) a cranking system. (Fig 2)
Fig 1 & 2
A generator commonly called a magneto is often designed to produce various voltages. The output may be as
low as 500 volts or as high as 1 megavolt. The current supplied by the megohmmeter is in the order of 5 to 10
milliamperes. The meter scale is calibrated: kilo-ohms (K W) and megohms(MW).
Working principle
The permanent magnets supply the flux for both the generator and the metering device. The voltage coils are
connected in series across the generator terminals. The current coil is arranged so that it will be in series with the
resistance to be measured. The unknown resistance is connected between the terminals L and E.
When the armature of the magnet is rotated, an emf is produced. This causes the current to flow through the
current coil and the resistance being measured. The amount of current is determined by the value of the resistance
and the output voltage of the generator.
129
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 20-25 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 20-25