Page 159 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 159
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Cycle
One complete wave of alternating current or voltage is known as one cycle. During the generation of one cycle
of AC there are two changes or alternations in polarity of the current . These equal but opposite halves of a
complete cycle are referred as alternations . In one cycle there are two half cycles known as positive& negative
half cycles.
Time period
The time required to produce one complete cycle is called time period .Or Time period is the reciprocal of frequency
.Its unit is second. Its symbol is T=1/f. Our supply frequency is 50 Hz and has a time period of 20ms
(T= 1/50 )
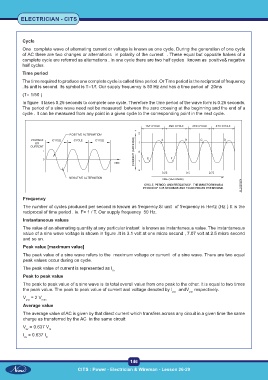
In figure it takes 0.25 seconds to complete one cycle. Therefore the time period of the wave form is 0.25 seconds.
The period of a sine wave need not be measured between the zero crossing at the beginning and the end of a
cycle . It can be measured from any point in a given cycle to the corresponding point in the next cycle.
Frequency
The number of cycles produced per second is known as frequency.SI unit of frequency is Hertz (Hz ) It is the
reciprocal of time period . ie. F= 1 / T. Our supply frequency 50 Hz.
Instantaneous values
The value of an alternating quantity at any particular instant is known as instantaneous value. The instantaneous
value of a sine wave voltage is shown in figure .It is 3.1 volt at one micro second , 7.07 volt at 2.5 micro second
and so on.
Peak value [maximum value]
The peak value of a sine wave refers to the maximum voltage or current of a sine wave. There are two equal
peak values occur during on cycle.
The peak value of current is represented as I
m
Peak to peak value
The peak to peak value of a sine wave is its total overall value from one peak to the other. It is equal to two times
the peak value. The peak to peak value of current and voltage denoted by I andV respectively.
p-p
p-p
V = 2 V
p-p max
Average value
The average value of AC is given by that direct current which transfers across any circuit in a given time the same
charge as transferred by the AC in the same circuit
V = 0.637 V
av m
I = 0.637 I m
av
146
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 26-29