Page 161 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 161
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
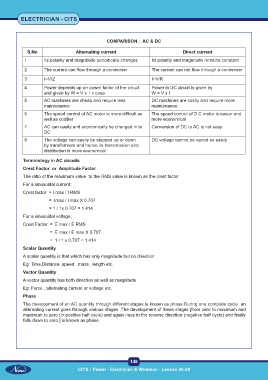
COMPARISON : AC & DC
S.No Alternating current Direct current
1 Its polarity and magnitude periodically changes Its polarity and magnitude remains constant
2 The current can flow through a condenser The current can not flow through a condenser
3 I=V/Z I=V/R
4 Power depends up on power factor of the circuit Power in DC circuit is given by
and given by W = V x I x cosө W = V x I
5 AC machines are cheap and require less DC machines are costly and require more
maintenance maintenance
6 The speed control of AC motor is more difficult as The speed control of D C motor is easier and
well as costlier more economical
7 AC can easily and economically be changed in to Conversion of DC to AC is not easy
DC
8 The voltage can easily be stepped up or down DC voltage cannot be varied so easily
by transformers and hence its transmission and
distribution is more economical
Terminology in AC circuits
Crest Factor or Amplitude Factor
The ratio of the maximum value to the RMS value is known as the crest factor
For a sinusoidal current ;
Crest factor = I max / I RMS
= Imax / I max X 0.707
= 1 / 1x 0.707 = 1.414
For a sinusoidal voltage;
Crest Factor = E max / E RMS
= E max / E max X 0.707
= 1 / 1 x 0.707 = 1.414
Scalar Quantity
A scalar quantity is that which has only magnitude but no direction
Eg: Time,Distance ,speed , mass , length etc.
Vector Quantity
A vector quantity has both direction as well as magnitude
Eg: Force , alternating current or voltage etc.
Phase
The development of an AC quantity through different stages is known as phase During one complete cycle an
alternating current goes through various stages .The development of these stages [from zero to maximum and
maximum to zero (in positive half cycle) and again rises in the reverse direction (negative half cycle) and finally
falls down to zero.] is known as phase
148
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 26-29