Page 166 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 166
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
In an AC is applied across pure capacitive circuit
Current will flow through the circuit is given by
I = V/Z
Z = Xc
I = V/Xc
Pure capacitive circuit the current does not remain in phase with the voltage but leads the voltage by 900 electrical
In pure capacitive circuit the power consumed in a circuit is zero , it has no resistance
Cosф = R/Z = 0
Power P = V x I x 0 = 0
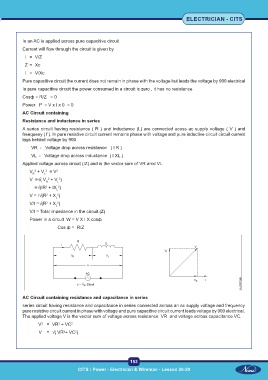
AC Circuit containing
Resistance and inductance in series
A series circuit having resistance ( R ) and inductance (L) are connected acoss ac supply voltage ( V ) and
freequeny ( f ). In pure resistive circuit current remains phase with voltage and pure inductive circuit circuit current
lags behind voltage by 900
VR - Voltage drop across resistance ( I R )
VL - Voltage drop across inductance ( I XL )
Applied voltage across circuit (IZ) and is the vector sum of VR amd VL
V 2 + V = V 2
2
R L
V =√( V + V )
2
2
L
R
=√(IR + IX )
2
2
L
V = I√(R + X )
2
2
L
V/I =√(R + X )
2
2
L
V/I = Total impedance in the circuit (Z)
Power in a circuit W = V X I X cosф
Cos ф = R/Z
AC Circuit containing resistance and capacitance in series
series circuit having resistance and capacitance in series connected across an ac supply voltage and frequency
pure resistive circuit current in phase with voltage and pure capacitive circuit current leads voltage by 900 electrical.
The applied voltage V is the vector sum of voltage across resistance VR and voltage across capacitance VC.
V = VR + VC 2
2
2
V = √( VR + VC )
2
2
153
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 26-29