Page 177 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 177
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
• For a given size the power out put is high in 3-phase motors whereas in single phase motors the power output
is low.
• Copper required for 3-phase transmission for a given power and distance is low when compared to single
phase system.
• 3-phase motor like squirrel cage induction motor is robust in construction and more are less maintenance
free.
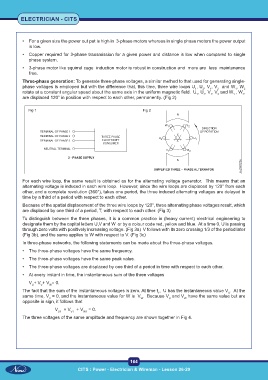
Three-phase generation: To generate three-phase voltages, a similar method to that used for generating single-
phase voltages is employed but with the difference that, this time, three wire loops U , U , V , V and W , W
1
1
1
2
2
2
rotate at a constant angular speed about the same axis in the uniform magnetic field. U , U , V , V and W , W ,
2
1
2
1
2
1
are displaced 120° in position with respect to each other, permanently. (Fig 2)
Fig 1 Fig 2
For each wire loop, the same result is obtained as for the alternating voltage generator. This means that an
alternating voltage is induced in each wire loop. However, since the wire loops are displaced by 120° from each
other, and a complete revolution (360°), takes one period, the three induced alternating voltages are delayed in
time by a third of a period with respect to each other.
Because of the spatial displacement of the three wire loops by 120°, three alternating phase voltages result, which
are displaced by one third of a period, T, with respect to each other. (Fig 3)
To distinguish between the three phases, it is a common practice in (heavy current) electrical engineering to
designate them by the capital letters U,V and W or by a colour code red, yellow and blue. At a time 0, U is passing
through zero volts with positively increasing voltage. (Fig 3a) V follows with its zero crossing 1/3 of the period later
(Fig 3b), and the same applies to W with respect to V. (Fig 3c)
In three-phase networks, the following statements can be made about the three-phase voltages.
• The three-phase voltages have the same frequency.
• The three-phase voltages have the same peak value.
• The three-phase voltages are displaced by one third of a period in time with respect to each other.
• At every instant in time, the instantaneous sum of the three voltages
V + V + V = 0.
U V W
The fact that the sum of the instantaneous voltages is zero. At time t , U has the instantaneous value V . At the
U
1
same time, V = 0, and the instantaneous value for W is V . Because V and V have the same value but are
U
V
W
W
opposite in sign, it follows that
V U1 + V + V = 0.
V1
W1
The three voltages of the same amplitude and frequency are shown together in Fig 4.
164
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 26-29