Page 178 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 178
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Fig 3 Fig 4
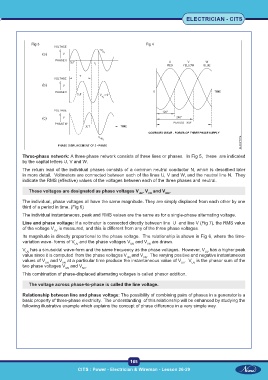
Three-phase network: A three-phase network consists of three lines or phases. In Fig 5, these are indicated
by the capital letters U, V and W.
The return lead of the individual phases consists of a common neutral conductor N, which is described later
in more detail. Voltmeters are connected between each of the lines U, V and W, and the neutral line N. They
indicate the RMS (effective) values of the voltages between each of the three phases and neutral.
These voltages are designated as phase voltages V , V and V .
UN VN WN
The individual, phase voltages all have the same magnitude. They are simply displaced from each other by one
third of a period in time. (Fig 6)
The individual instantaneous, peak and RMS values are the same as for a single-phase alternating voltage.
Line and phase voltage: If a voltmeter is connected directly between line U and line V (Fig 7), the RMS value
of the voltage V is measured, and this is different from any of the three phase voltages.
UV
Its magnitude is directly proportional to the phase voltage. The relationship is shown in Fig 6, where the time-
variation wave- forms of V and the phase voltages V and V are drawn.
UN
UV
VN
V has a sinusoidal wave-form and the same frequency as the phase voltages. However, V has a higher peak
UV
UV
value since it is computed from the phase voltages V and V . The varying positive and negative instantaneous
UN
VN
values of V and V at a particular time produce the instantaneous value of V . V is the phasor sum of the
UV
UV
UN
VN
two phase voltages V and V .
UN NV
This combination of phase-displaced alternating voltages is called phasor addition.
The voltage across phase-to-phase is called the line voltage.
Relationship between line and phase voltage: The possibility of combining pairs of phases in a generator is a
basic property of three-phase electricity. The understanding of this relationship will be enhanced by studying the
following illustrative example which explains the concept of phase difference in a very simple way.
165
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 26-29