Page 250 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 250
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
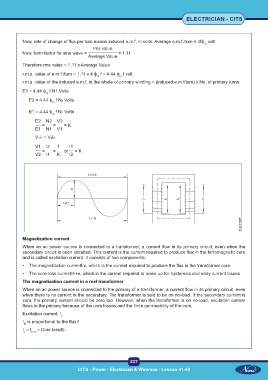
Now, rate of change of flux per turn means induced e.m.f. in volts. Average e.m.f./turn = 4ff volt
m
rms value
Now, form factor for sine wave = = 1.11
Average Value
Therefore rms value = 1.11 x Average Value
r.m.s. value of e.m.f./turn = 1.11 x 4 f f = 4.44 f f volt
m m
r.m.s. value of the induced e.m.f. in the whole of primary winding = (induced e.m.f/turn) x No. of primary turns
E1 = 4.44 f f N1 Volts
m
E2 = 4.44 f f N2 Volts
m
E1 = 4.44 f f N1 Volts
m
E2 N2 V2
= = = K
E1 N1 V1
V1I1 = V2I2
V1 I2 1 I1
= = or = K
V2 I1 K I2
Magnetization current
When an ac power source is connected to a transformer, a current flow in its primary circuit, even when the
secondary circuit is open circuited. This current is the current required to produce flux in the ferromagnetic core
and is called excitation current. It consists of two components:
• The magnetization currentIm, which is the current required to produce the flux in the transformer core
• The core-loss currentIh+e, which is the current required to make up for hysteresis and eddy current losses
The magnetization current in a real transformer
When an ac power source is connected to the primary of a transformer, a current flow in its primary circuit, even
when there is no current in the secondary. The transformer is said to be on no-load. If the secondary current is
zero, the primary current should be zero too. However, when the transformer is on no-load, excitation current
flows in the primary because of the core losses and the finite permeability of the core.
Excitation current, I
o
I is proportional to the flux f
M
I = I = Core loss/E1
h+e
c
237
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 41-49 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 41-49