Page 100 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 100
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
R 2
Starting torque R 2 2 X as fractional slip S = 1
2
2
1
Maximum torque
X 2
where X2 in inductive reactance of the rotor at standstill and is constant.
Rotor copper loss: Rotor copper loss is the loss of power taking place in the rotor due to its resistance and the
rotor current. Though the resistance of the rotor for a squirrel cage motor remains constant, the current in the rotor
depends upon the slip, transformation ratio between the stator and rotor voltages and the inductive reactance of
the rotor circuit.
Insulation test on 3 phase induction motors
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to:
• state the necessity for and the method of testing continuity and insulation resistance in a 3-phase induction
motor
• state the necessity of continuity test before insulation test.
Necessity of continuity test before insulation test: While testing the insulation resistance between the winding and
the frame, it is the usual practice to connect one prod of the Megger to the frame and the other prod to any one of
the terminals of the winding. Likewise, when testing insulation resistance between windings, it is the usual practice
to connect the two prods of the Megger to any two ends of a different winding. In all the cases it is assumed that
the windings are in sound condition and the two ends of the same winding will be having continuity. However, it
is possible the winding may have a break, and part of the winding may have a higher insulation resistance and
the other part might have been grounded. Hence, to increase the reliability of the insulation resistance test, it is
recommended that continuity test may be conducted in the motor before the insulation test, to be sure, that the
winding is sound and the insulation resistance includes the entire winding.
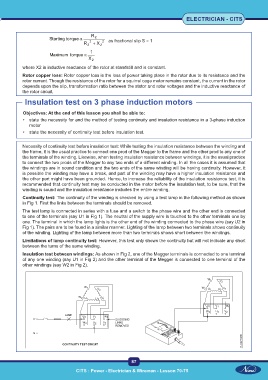
Continuity test: The continuity of the winding is checked by using a test lamp in the following method as shown
in Fig 1. First the links between the terminals should be removed.
The test lamp is connected in series with a fuse and a switch to the phase wire and the other end is connected
to one of the terminals (say U1 in Fig 1). The neutral of the supply wire is touched to the other terminals one by
one. The terminal in which the lamp lights is the other end of the winding connected to the phase wire (say U2 in
Fig 1). The pairs are to be found in a similar manner. Lighting of the lamp between two terminals shows continuity
of the winding. Lighting of the lamp between more than two terminals shows short between the windings.
Limitations of lamp continuity test: However, this test only shows the continuity but will not indicate any short
between the turns of the same winding.
Insulation test between windings: As shown in Fig 2, one of the Megger terminals is connected to one terminal
of any one winding (say U1 in Fig 2) and the other terminal of the Megger is connected to one terminal of the
other windings (say W2 in Fig 2).
87
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 70-75 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 70-75