Page 221 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 221
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Oscillator
It is an electronic circuit which generates the oscillating pulses either through an IC circuit or a transistorized
circuit. This oscillations are the production of alternate pulse of positive and negative (ground) voltage peaks of a
battery and at a specified frequency (No.of positive peaks per second). These are generally in the form of square
waves and the inverters are called square wave inverters.
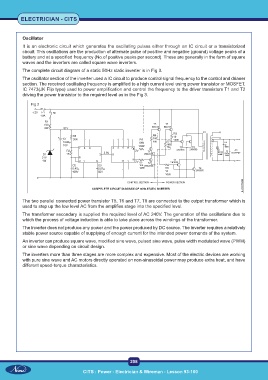
The complete circuit diagram of a static 50Hz static inverter is in Fig 3.
The oscillator section of the inverter used a IC circuit to produce control signal frequency to the control and drianer
section. The received oscillating frequency is amplified to a high current level using power transistor or MOSFET.
IC 7473(JK Flip type) used to power amplification and control the frequency to the driver transistors T1 and T2
driving the power transistor to the required level as in the Fig 3.
Fig 3
The two parallel connected power transistor T5, T6 and T7, T8 are connected to the output transformer which is
used to step up the low level AC from the amplifies stage into the specified level.
The transformer secondary is supplied the required level of AC 240V. The generation of the oscillations due to
which the process of voltage induction is able to take place across the windings of the transformer.
The inverter does not produce any power and the power produced by DC source. The inverter requires a relatively
stable power source capable of supplying of enough current for the intended power demands of the system.
An inverter can produce square wave, modified sine wave, pulsed sine wave, pulse width modulated wave (PWM)
or sine wave depending on circuit design.
The inverters more than three stages are more complex and expensive. Most of the electric devices are working
with pure sine wave and AC motors directly operated on non-sinusoidal power may produce extra heat, and have
different speed-torque characteristics.
208
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 93-100