Page 25 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 25
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
PN Junction - semi conductor diodes
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• explain diffusion in pn junction and barrier potential
• explain forward and reverse biasing of pn junction and semi conductor diodes and its vi characteristics
• state the applications specifications and classification of diodes
• state the method of testing diode and identifying the polarity
• state special diodes and their functions and PIV.
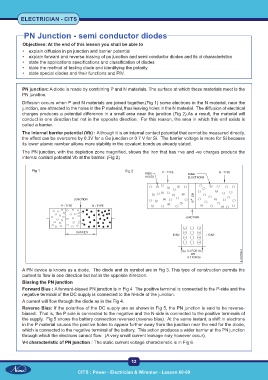
PN junction: A diode is made by combining P and N materials. The surface at which these materials meet is the
PN junction.
Diffusion occurs when P and N materials are joined together.(Fig 1) some electrons in the N material, near the
junction, are attracted to the holes in the P material, thus leaving holes in the N material. The diffusion of electrical
charges produces a potential difference in a small area near the junction (Fig 2).As a result, the material will
conduct in one direction but not in the opposite direction. For this reason, the area in which this emf exists is
called a barrier.
The internal barrier potential (Vb) : Although it is an internal contact potential that cannot be measured directly,
the effect can be overcome by 0.3V for a Ge junction or 0.7 V for Si. The barrier voltage is more for Si because
its lower atomic number allows more stability in the covalent bonds as already stated.
The PN junction, with the depletion zone magnified, shows the iron that has +ve and -ve charges produce the
internal contact potential Vb at the barrier. (Fig 2)
Fig 1 Fig 2
A PN device is knows as a diode. The diode and its symbol are in Fig 3. This type of construction permits the
current to flow in one direction but not in the opposite direction.
Biasing the PN junction
Forward Bias : A forward-biased PN junction is in Fig 4 The positive terminal is connected to the P-side and the
negative terminal of the DC supply is connected to the N-side of the junction.
A current will flow through the diode as in the Fig 4.
Reverse Bias: If the polarities of the DC supply are as shown in Fig 5, the PN junction is said to be reverse-
biased. That is, the P side is connected to the negative and the N-side is connected to the positive terminals of
the supply. Fig 5 shows the battery connection reversed (reverse bias). At the same instant, a shift in electrons
in the P material causes the positive holes to appear further away from the junction near the end for the diode,
which is connected to the negative terminal of the battery. This action produces a wider barrier at the PN junction
through which the electrons cannot flow. (A very small current leakage may however occur).
V-I characteristic of PN junction : The static current voltage characteristic is in Fig 6.
12
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69