Page 313 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 313
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
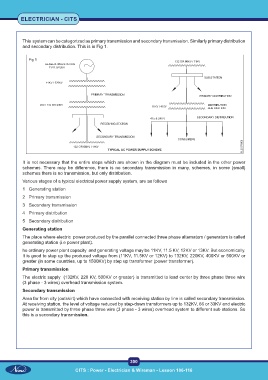
This system can be categorized as primary transmission and secondary transmission. Similarly primary distribution
and secondary distribution. This is in Fig 1.
Fig 1
It is not necessary that the entire steps which are shown in the diagram must be included in the other power
schemes. There may be difference, there is no secondary transmission in many, schemes, in some (small)
schemes there is no transmission, but only distribution.
Various stages of a typical electrical power supply system, are as follows
1 Generating station
2 Primary transmission
3 Secondary transmission
4 Primary distribution
5 Secondary distribution
Generating station
The place where electric power produced by the parallel connected three phase alternators / generators is called
generating station (i.e power plant).
he ordinary power plant capacity and generating voltage may be 11KV, 11.5 KV, 12KV or 13KV. But economically.
It is good to step up the produced voltage from (11KV, 11.5KV or 12KV) to 132KV, 220KV, 400KV or 500KV or
greater (in some countries, up to 1500KV) by step up transformer (power transformer).
Primary transmission
The electric supply (132KV, 220 KV, 500KV or greater) is transmitted to load center by three phase three wire
(3 phase - 3 wires) overhead transmission system.
Secondary transmission
Area far from city (outskirt) which have connected with receiving station by line is called secondary transmission.
At receiving station, the level of voltage reduced by step-down transformers up to 132KV, 66 or 33KV and electric
power is transmitted by three phase three wire (3 phase - 3 wires) overhead system to different sub stations. So
this is a secondary transmission.
300
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 106-116