Page 53 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 53
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
For instance, if we assume that input resistance of 200W, a load resistance of 50K and a current gain of 0.98, the
voltage gain is 0.98 x 50k/200 = 245
Voltage amplifier: An amplifier is a circuit that incorporates one or more transistors and is designed to increase
an alternating signal applied to the input terminals. It is called a voltage amplifier. If the size or magnitude of the
output voltage is considerably greater than the input voltage, it is called the voltage gain of the amplifier.
Fig 8
The main function of a voltage amplifier is to produce a given gain with the minimum of distortion, i.e. the output
voltages should have the same wave-form as the input wave-form, but should of course be much higher in
magnitude. Examples for the voltage amplifier are the common base and the common emitter amplifiers.
Current amplifier: The function of the current amplifier is when the current injected in the base, load can influence
to much greater current to flow in the emitter-collector circuit.
The remarkable result is that, if the base current is increased by a certain proportion, the base current in the
collector current gives rise to a corresponding, but much larger changes in the collector current. We have achieved
current amplification. The ratio of the output current to the input current is called the current gain of the amplifier.
An example for the current amplifier is the common-emitter, common-collector amplifier. The current gain of
common-emitter amplifier is 50 to 300 and that of the common-collector amplifier is 50 to 500.
Power amplifier : Power amplifiers are used to drive the output mechanism, e.g. a loudspeaker, a pair of
earphones, a moving coil meter or some other type of indicating device. The main function of a power amplifier
is to deliver a good deal of undistorted power into the output device or load circuit. Examples for the power
amplifiers are class A, class B, class AB and class C.
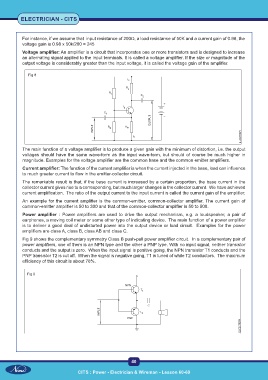
Fig 9 shows the complementary symmetry Class B push-pull power amplifier circuit. In a complementary pair of
power amplifiers, one of them is an NPN type and the other a PNP type. With no input signal, neither transistor
conducts and the output is zero. When the input signal is positive going, the NPN transistor T1 conducts and the
PNP transistor T2 is cut off. When the signal is negative going, T1 is tuned of while T2 conductors. The maximum
efficiency of this circuit is about 78%.
Fig 9
40
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69