Page 50 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 50
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
The response of the collector current Ic to the input wave-form, together with its time relationship to that waveform,
is in Fig 4c. The current does not immediately respond to the input signal. Instead, there is a delay, and the time
that elapses during this delay, together with the time required for the current to rise to 10 percent of its maximum
(saturation) value ICS = Vcc/RL, is called the delay time td. The current waveform has a nonzero rise time tr
which is the time required for the current to rise from 10 to 90 percent of ICS. The total turn-on time tON is the
sum of the delay and rise time,
t = t + t r
ON
d
When the input signal returns to its initial state at t = T
(Fig 4b), the current again fails to respond immediately. The interval which elapses between the transition of the
input waveform and the time when ic has dropped to 90 percent of ICS is called the storage time ts. The storage
interval is followed by the fall time tt, which is the time required for ic to fall from 90 to 10 percent of ICS. The turn
off time to tOFF is defined as the sum of the storage and fall times,
t OFF = t + t F
s
The application of transistor switch: The transistor switch is used
• as an electronic on and off switch
• in the stable, mono-stable and bi-stable or filp-flop multi-vibrator circuits
• in the counter and pulse generator circuit
• in the clipping circuits
• as a sweep starting switch in the cathode ray oscilloscope equipment
• as a relay, but unlike the mechanical relay, the transistor has no moving mechanical parts.
Series voltage regulator
Voltage regulated power supply using zener diode is the simplest form of voltage regulator. But, zener voltage
regulators have two main disadvantages:
1 When the load current requirement is higher, say of the order of a few amperes, the zener regulator requires
a very high wattage zener diode capable of handling high current.
2 In a zener regulator, the load resistor sees an output impedance of approximately the zener impedance, RZ
which ranges from a few ohms to a few tens of ohms (typically 5W to 25W). This is a considerably high output
impedance because the output impedance of a ideal power supply should be zero ohms.
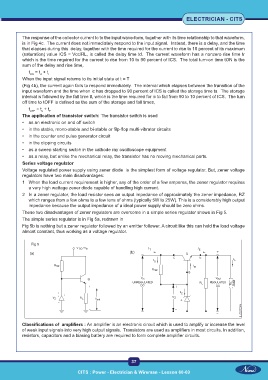
These two disadvantages of zener regulators are overcome in a simple series regulator shown in Fig 5.
The simple series regulator is in Fig 5a, redrawn in
Fig 5b is nothing but a zener regulator followed by an emitter follower. A circuit like this can hold the load voltage
almost constant, thus working as a voltage regulator.
Fig 5
Classifications of amplifiers : An amplifier is an electronic circuit which is used to amplify or increase the level
of weak input signals into very high output signals. Transistors are used as amplifiers in most circuits. In addition,
resistors, capacitors and a biasing battery are required to form complete amplifier circuits.
37
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69