Page 46 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 46
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
The collector current Ic will be approximately equal to IE.
Notice that bdc does not appear in the formula for emitter current. This means that the circuit is not dependent
on variations in bdc. This means that the divider-biased transistor has a stable Q point.
Because of the stable Q point, voltage-divider bias is the most preferred form of bias in linear transistor circuits.
Hence, divider bias is used almost universally.
Transistor characteristics
In a transistor there are two PN junctions followed by three voltage parameters V , V , V and three current
BE
BC
CE
parameters I , I , I is in Fig 6.
B C E
Any change in any one parameter causes changes in all the other parameters. Hence it is not very easy to
correlate the effect of one parameter with the others. To have a clear understanding of their relationship a minimum
of two characteristics graphs should be plotted for any transistor. They are,
– Input characteristics
– Output characteristics
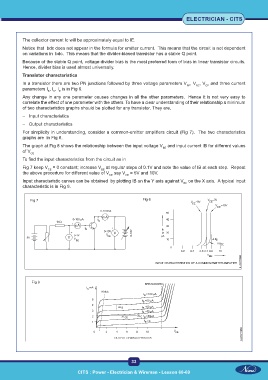
For simplicity in understanding, consider a common-emitter amplifiers circuit (Fig 7). The two characteristics
graphs are in Fig 8.
The graph at Fig 8 shows the relationship between the input voltage V and input current IB for different values
BE
of V
CE
To find the input characteristics from the circuit as in
Fig 7 keep V = 0 constant; increase V at regular steps of 0.1V and note the value of IB at each step. Repeat
BE
CE
the above procedure for different value of V say V = 5V and 10V.
CE CE
Input characteristic curves can be obtained by plotting IB on the Y axis against V on the X axis. A typical input
BE
characteristic is in Fig 9.
Fig 7 Fig 8
Fig 9
33
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69