Page 42 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 42
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Transistors data books give information for any particular transistor as to whether it is a AF of RF transistor.
Testing of transistor : A transistor can be tested for all specifications shown in the data book. But verification of
almost all specifications, except a few requires an elaborate step up and can damage the transistor permanently.
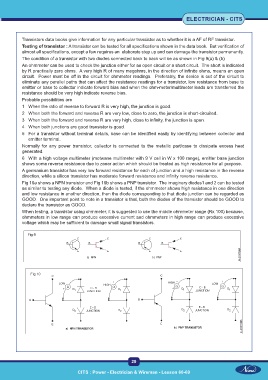
The condition of a transistor with two diodes connected back to back will be as shown in Fig 9(a) & (b)
An ohmmeter can be used to check the junction either for an open circuit or a short circuit. The short is indicated
by R practically zero ohms. A very high R of many megohms, in the direction of infinite ohms, means an open
circuit. Power must be off in the circuit for ohmmeter readings. Preferably, the device is out of the circuit to
eliminate any parallel paths that can affect the resistance readings for a transistor, low resistance from base to
emitter or base to collector indicate forward bias and when the ohm-meter/multimeter leads are transferred the
resistance should be very high indicate reverse bias.
Probable possibilities are
1 When the ratio of reverse to forward R is very high, the junction is good.
2 When both the forward and reverse R are very low, close to zero, the junction is short-circuited.
3 When both the forward and reverse R are very high, close to infinity, the junction is open.
4 When both junctions are good transistor is good.
5 For a transistor without terminal details, base can be identified easily by identifying between collector and
emitter terminal.
Normally for any power transistor, collector is connected to the metallic part/case to dissipate excess heat
generated.
6 With a high voltage multimeter (motwane multimeter with 9 V cell in W x 100 range), emitter base junction
shows some reverse resistance due to zener action which should be treated as high resistance for all purpose.
A germanium transistor has very low forward resistance for each of junction and a high resistance in the reverse
direction, while a silicon transistor has moderate forward resistance and infinity reverse resistance.
Fig 10a shows a NPN transistor and Fig 10b shows a PNP transistor. The imaginary diodes1 and 2 can be tested
as similar to testing any diode. When a diode is tested, if the ohmmeter shows high resistance in one direction
and low resistance in another direction, then the diode corresponding to that diode junction can be regarded as
GOOD. One important point to note in a transistor is that, both the diodes of the transistor should be GOOD to
declare the transistor as GOOD.
When testing, a transistor using ohmmeter, it is suggested to use the middle ohmmeter range (Rx 100) because,
ohmmeters in low range can produce excessive current and ohmmeters in high range can produce excessive
voltage which may be sufficient to damage small signal transistors.
Fig 9
Fig 10
29
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69