Page 39 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 39
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
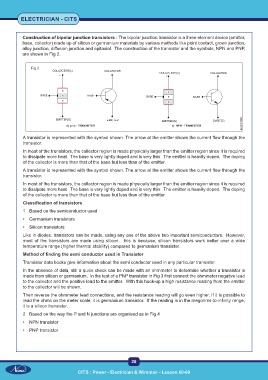
Construction of bipolar junction transistors : The bipolar junction transistor is a three-element device (emitter,
base, collector) made up of silicon or germanium materials by various methods like point contact, grown junction,
alloy junction, diffusion junction and epitaxial. The construction of the transistor and the symbols, NPN and PNP,
are shown in Fig 2.
Fig 2
A transistor is represented with the symbol shown. The arrow at the emitter shows the current flow through the
transistor.
In most of the transistors, the collector region is made physically larger than the emitter region since it is required
to dissipate more heat. The base is very lightly doped and is very thin. The emitter is heavily doped. The doping
of the collector is more than that of the base but less than of the emitter.
A transistor is represented with the symbol shown. The arrow at the emitter shows the current flow through the
transistor.
In most of the transistors, the collector region is made physically larger than the emitter region since it is required
to dissipate more heat. The base is very lightly doped and is very thin. The emitter is heavily doped. The doping
of the collector is more than that of the base but less than of the emitter.
Classification of transistors
1 Based on the semiconductor used
• Germanium transistors
• Silicon transistors
Like in diodes, transistors can be made, using any one of the above two important semiconductors. However,
most of the transistors are made using silicon. this is because, silicon transistors work better over a wide
temperature range (higher thermal stability) compared to germanium transistor.
Method of finding the semi conductor used in Transistor
Transistor data books give information about the semi conductor used in any particular transistor.
In the absence of data, still a quick check can be made with an ohmmeter to determine whether a transistor is
made from silicon or germanium. In the test of a PNP transistor in Fig 3 first connect the ohmmeter negative lead
to the collector and the positive lead to the emitter. With this hook-up a high resistance reading from the emitter
to the collector will be shown.
Then reverse the ohmmeter lead connections, and the resistance reading will go even higher. If it is possible to
read the ohms on the meter scale, it is germanium transistor. If the reading is in the megohms-to-infinity range,
it is a silicon transistor.
2 Based on the way the P and N junctions are organised as in Fig 4
• NPN transistor
• PNP transistor
26
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69