Page 35 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 35
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Current rating of diodes in bridge rectifiers : As in the case of a two diode fullwave rectifier even in a bridge
rectifier is in Fig 5, diode pairs D , D and D D carry half the total load current1. This is because each diode pair
2
4
1
3
is conducting only during one half of the AC input cycle.
The only disadvantage of bridge rectifiers, D , D and D , D is that, this circuit uses four diodes for full wave
2
3
1
4
rectification instead of two as in two-diode fullwave rectifier. But this disadvantage is compensated by the simple
transformer requirement of the bridge rectifier and higher DC output level. Hence, bridge rectifiers are the most
popular AC to DC rectifiers for most applications.
Encapsulated bridge rectifiers are available as a single pack with two terminals for AC input and two terminals for
DC output.
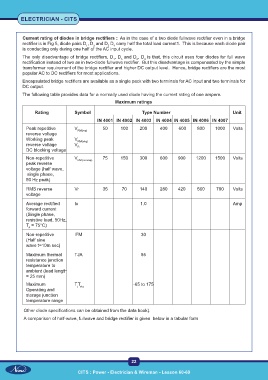
The following table provides data for a normally used diode having the current rating of one ampere.
Maximum ratings
Rating Symbol Type Number Unit
IN 4001 IN 4002 IN 4003 IN 4004 IN 4005 IN 4006 IN 4007
Peak repetitive V RM(rep) 50 100 200 400 600 800 1000 Volts
reverse voltage
Working peak V RM(wkg)
reverse voltage V R
DC blocking voltage
Non-repetitive V RM (nonrep) 75 150 300 600 900 1200 1500 Volts
peak reverse
voltage (half wave,
single phase,
50 Hz peak)
RMS reverse Vr 35 70 140 280 420 560 700 Volts
voltage
Average rectified Io 1.0 Amp
forward current
(Single phase,
resistive load, 50Hz,
T = 75°C)
A
Non-repetitive IFM 30
(Half sine
wave t=10m sec)
Maximum thermal TJA 85
resistance junction
temperature to
ambient (lead length
= 25 mm)
Maximum TT -65 to 175
j stg
Operating and
storage junction
temperature range
Other diode specifications can be obtained from the data book).
A comparison of half-wave, fullwave and bridge rectifier is given below in a tabular form
22
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69